Fire extinguishing systems definition. Fire alarm and fire extinguishing means automatic fire extinguishing system
From ancient times to the present, fires have been a serious problem in people's lives. Some especially strong fires go down in history and change the life of entire cities and even states. So it was, for example, with the Great Fire of London in 1666 or with the famous fire of Moscow during the Patriotic War of 1812. Therefore, it is logical that each property owner seeks to protect himself from fire.
Modern fire protection systems provide high level security, but the issue of economic efficiency in this case is no less important. It is unlikely that someone will want to pay a lot of money for an automatic fire extinguishing installation if the probability of a fire at this particular facility is extremely small.
The main criterion when choosing a fire extinguishing system and the amount of money that the owner of the object is willing to spend on it is the potential damage that may be caused in the event of a fire. In order to navigate in different ways fire systems, the formula S \u003d A + B is used, where A is the estimated losses (thousand rubles per year) from a fire at the protected facility after the system is triggered, and B is the development, installation and annual maintenance costs of the automatic fire extinguishing installation.
It should also be noted that the alleged losses include not only the actual destruction of property, but also the income that will be lost due to failure of the burned equipment. When analyzing various options for fire extinguishing systems, the one that assumes the lowest S value will be most preferable.
Often you can find an option in which the object is installed only fire alarm. It is an effective means of detecting a fire, but this is where its functions end, since it cannot actually extinguish a fire. At the same time, the state system fire brigade not as fast as many property owners would like - the average arrival time of the fire brigade is about 10 minutes. This is a significant period of time during which many values \u200b\u200bcan be destroyed permanently by fire.
In addition, in recent years there has been a tendency to increase this time. In large and medium-sized cities, population growth leads to the fact that the number of cars increases, and the throughput of roads does not change. As a result, there are traffic jams that are difficult for a fire engine to overcome even with a flashing light and a siren. In rural areas, the situation is no better, but the point is not traffic jams. Lack of road repairs, understaffed crews, outdated equipment - all this is the reason for the increase in the average time of arrival to a fire.
In order to completely protect themselves from fire or at least minimize its consequences, automatic fire extinguishing installations (AUP) are used at various facilities. They are able to independently detect and extinguish a fire without human intervention. It often happens that the operator learns about the fire after it is extinguished.

Systems automatic fire fighting differ from each other in several ways. Although they are designed to serve one purpose, their device is sometimes fundamentally different from each other. The table below shows the most common classification methods for automatic fire extinguishing installations:
|
AUP classification |
|||
|
By type of extinguishing agent |
By design |
Extinguishing Method |
By way of commissioning |
|
Sprinkler |
By volume |
Manual start |
|
|
Deluge |
By area |
Auto start |
|
|
Powder |
Aggregate |
Locally to the fire |
Remote start |
|
Modular |
Combined method |
||
|
Aerosol |
|||
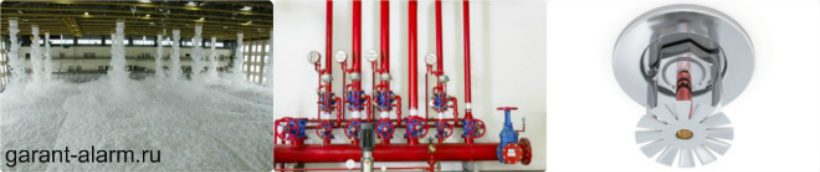
The most popular, reliable and simple automatic fire extinguishing system is the sprinkler. These installations, due to their effectiveness, are used in almost any facility, including of particular importance. According to statistics, more than 90% of fires in the world are extinguished by just such systems.
Sprinkler units operate according to the following principle. Pipes filled with water or an aqueous solution that is under pressure are mounted throughout the room. At certain intervals, locks are installed in the pipes, which serve as thermal sensors. In most cases, they are designed for temperatures around 70 ° C.
When a fire occurs, the sprinkler that is located closest to the source of fire is triggered. For example, if pipes are laid under the ceiling, and a fire starts on the floor, then the thermal lock will collapse in 2-3 minutes. All pipes of the system covering the room are connected to a common highway in which automation equipment is located. The line, in turn, is connected to a pump, which creates pressure in the entire automatic fire extinguishing installation.
Under normal conditions, the system is pressurized, with all safety valves closed. When a fire starts, the thermal lock starts to heat up. The design of the lock is a glass flask filled with a special substance, and a stopper-valve.
When heated, the substance in the flask expands and when a certain temperature is reached (which is determined by the brand of the castle and the type of substance) it destroys the glass shell. The plug-valve is pushed out of the pipeline, and water immediately begins to flow into the fire.

Automatic sprinkler fire extinguishing installations are good in that in a fire only those locks near which there is fire are destroyed. This significantly saves water consumption and allows you to protect other materials from it that the fire has not reached.
Although the water in the system is under pressure, its supply will soon run out, since after opening even one or two locks, a significant amount of extinguishing agent falls on the fire. To ensure that the fire is extinguished, pressure sensors are installed in the pipelines. They fix its decrease, which inevitably occurs after the destruction of the thermal lock, and sends the corresponding signal to the control unit.
The unit starts up the main pump or turns on the backup pump if the first one fails. Pump operating time, as a rule, is from half an hour to an hour. One thermal lock can cover an area of \u200b\u200b9 to 16 m².
Despite the general principle of operation of thermal locks, sprinkler systems can differ from each other in many parameters. For example, they can be coated with a special composition that protects them from corrosion, or made of refractory material. The dimensions of the sprinklers are of great importance, as well as the scope of their application - the systems for offices and warehouses are very different from each other. Modern sprinkler systems are compact and almost do not attract attention with their appearance.

For objects that do not have heating, the use of water in automatic fire extinguishing installations loses its meaning because of its possible freezing. In these cases, compressed air is supplied to the sprinklers, which presses on the shutter of the protective valve. Water is higher up the pipes and is fenced from the “air plug” by a special valve. The main fluid reservoir is located in a heated room. In addition, the system further includes a compressor for maintaining air pressure. Otherwise, the principle of operation of such a sprinkler system is identical to a system operating only on water.
Speaking about the advantages of sprinkler fire extinguishing systems, it is worth mentioning their disadvantages. Imagine that a fire occurred in a warehouse of petroleum products or other flammable liquids. In this case, the fire will spread quickly enough, without waiting for each thermal lock to work.
How to protect materials? To do this, use deluge automatic fire extinguishing installations, which are also called flooding. The principle of their work is to use special fire sensors located throughout the room. The valves of the system do not open as a result of heat damage, like sprinklers, but at the command of the control unit.
Having received information from the sensors about the start of the fire, the controller opens all the valves, regardless of which zone of the object the fire started. The room is completely flooded with water or a special solution, not allowing the flame to spread to neighboring objects.
To protect material assets and at the same time to effectively extinguish the fire, special installations are used that combine the features of sprinkler and deluge fire extinguishing systems. They are also called pre-action systems, and represent one deluge valve on a common fire extinguishing line, and classic “on-site” sprinkler valves. In addition, the premises are installed thermal sensorsset to a value lower than the temperature of the destruction of thermal locks.
In the normal state, the system is not filled with water, unlike sprinkler systems in their pure form. In the event of a fire, first of all, the sensor of the deluge system is triggered, since its temperature is lower than that of sprinklers.
This sensor opens the deluge valve in the common line, as a result of which water enters the system, but does not pass further than the sprinklers. If during this time the fire is not detected, or they do not have time to extinguish with primary means, the temperature will continue to rise, and the destruction of sprinklers will begin. If the fire is extinguished in advance, extinguishing with large volumes of water will not be required, and this will save property.
To avoid possible water consumption and damage to property, additional protective elements can be added to the deluge valve system for which different operating conditions are set. The number and type of protective elements are determined by the safety requirements at each specific facility. Thanks to such equipment, you can get a reliable fire extinguishing system with flexible settings.
For example, pre-action installations are often used in libraries, storages or museums where water can completely destroy existing values. Also in these systems, equipment is additionally installed to create finely atomized water, which cools the fire in the same way as ordinary water, but otherwise acts as a non-combustible gas and does not harm paper or paintings. The extinguishing process is controlled by temperature sensors, which when it is reduced to a predetermined value completely shut off the water supply.
If the fire is not extinguished to the end, and the temperature begins to rise again, the automation will restart the pumps. Such systems, already more advanced, work without human intervention and are called cyclic. They are especially valuable in that they can be used to protect repositories of harmful and toxic substances, where the constant presence of a person is undesirable or excluded. Water or foam is used as extinguishing agent in such systems.
Ordinary sprinkler or deluge systems can also use foam. This requires special equipment for the formation of foam: a reservoir for foamy concentrate, a dispenser for mixing the concentrate with water, as well as valves, electric drives and a control and automation system.
A more advanced automatic fire extinguishing installation is a system using finely dispersed water. Water has such a name because it is supplied under high pressure through very narrow nozzles. Thus, water enters the combustion zone in the form of tiny droplets and more effectively displaces oxygen.
Water can also be mixed with non-combustible gas, making the quenching process even faster. The equipment for such systems is more complicated than for conventional sprinkler or deluge systems, however, these costs are offset by a smaller tank volume and low water consumption. In addition, the high rate of extinction significantly reduces material damage from fire and water.
Finally, automatic installations gas fire non-combustible gases - nitrogen, carbon dioxide, some inert gases, etc. are used as the main substance. Similar systems are used where the use of water can cause even greater damage than the fact of a fire. The disadvantage of such systems is the strict requirements for the evacuation of personnel, since gases block the access of oxygen not only to fire, but also to people. A variety of gas plants are powder systems that use a mixture of dry non-combustible materials instead of gas. Most often they are used to extinguish closed electrical installations, the use of water in which can lead to a short circuit
 .
.
The legislation of the Russian Federation obliges owners of facilities to equip them with automatic fire extinguishing means, the options for which are determined by the purpose of the building and the potential damage that may be caused by a fire.
For some rooms, the rules are limited by the requirement to install fire shields with the simplest means of protection, but for many objects, especially in industry, automatic fire extinguishing installations are required. Unfortunately, they are not always installed, as required by regulatory enactments.
Some property owners do not have the means to do this, while others buy cheaper and less reliable installations. Worst of all, and this is common enough when owners deliberately do not use protection, believing that the fire will not affect them.
Despite the fact that the introduction of automatic fire extinguishing installations in critical facilities has long been enshrined in law, there are still designers and property owners who stubbornly do not want to spend money on this. They expect that the fire will bypass them, however, as often happens, it comes to those who did not take care of their safety in advance.
That is why the development of a fire extinguishing system must be approached from the opposite side, considering that a fire will occur. And it will not just happen, but will be as strong as possible in order to destroy all buildings and values. Based on this, the optimal composition of the fire system should be chosen. Typically, developers are guided by the following criteria:
- Safety for people;
- Security for property;
- Extinguishing rate;
- The complexity of installation and maintenance;
- Environmental Safety;
- Price.
After that, the study of the features of a particular object begins. Consider the choice of an automatic fire extinguishing installation for such a building, where a lot of paper documents or similar values \u200b\u200bare stored - a museum, library or archive.

Fire extinguishing system implementation in libraries and similar facilities
Modern technology involves the storage of information on special media. Thousands of pages of information easily fit on a small memory card that weighs less than one gram. However, there is a lot of information that is forcedly stored on paper. These can be various archival documents that should be stored for several years, but they are in no hurry to translate them into electronic form.
It can be money in a bank, or books in a library. Finally, many paper media are no less historical value than the information they contain. Imagine the original work of Shakespeare or Pushkin, reflecting the spirit of those times, and significance fire protection will increase at times. Also in this category can be attributed paintings and in general most of the values \u200b\u200bstored in museums.
All this makes libraries, banks, archives, museums and similar objects the premises where the installation of automatic fire extinguishing systems is strictly required. In addition to actually fighting fire, they are subject to stringent requirements for the speed of operation and the type of extinguishing agent.
The speed should be minimal after the detection of fire, and the extinguishing agent should not damage the storage media. This is especially true of repositories of historical documents, since even a slight change in temperature or humidity in them can lead to destruction of paper.
Thus, the listed factors form two basic requirements for automatic fire extinguishing installations at facilities of this type:
- The extinguishing agent must extinguish the fire extremely quickly and prevent its spread;
- The extinguishing agent must not cause damage to property.

From these requirements it is clear that water - such a popular means of combating fire - is not suitable for use on objects of this kind. The reason is clear: under the influence of water, the paper softens, as well as the ink on it spreads and spreads. As a result of this, not only information can be lost, but also the medium itself, which is completely unacceptable for storing values. In addition, water can trigger complex chemical processes in which destructive substances can penetrate deep into even paper untouched by fire and water, which in the future will also lead to their loss.
Foams or powders are more attractive extinguishing agents, but even upon closer examination they are excluded from the list of extinguishing candidates. The fact is that they all fight fire through a chemical reaction. At the same time, the powder does not make out what needs to be extinguished, and equally affects both fire and other substances in the room. Another minus in favor of aerosols is the high starting temperature of these substances. Sometimes it is so high that they themselves can become sources of ignition of paper.
It is also undesirable to use systems based on aqueous salts of metals of the first group of the periodic table - sodium or potassium. They act on fire chemical methods even more actively than aerosols and powders, but on other substances, their effect is extremely strong. In addition, they cause inflammation of the eyes and skin of a person, which forces them to be abandoned while protecting libraries and repositories of valuable materials.
As a result, non-combustible gases are best suited for the role of extinguishing agent for objects of this purpose. True, this method has its opponents, who argue that gas installations do well only with open fire and poorly detect smoldering sources. Moreover, the previous legislative norms prescribed to have additional facilities at the facilities for the production of finely dispersed water to guarantee the suppression of any fire. This approach, indeed, allows you to cope with fire in all cases, however, the risk of damage to material assets is also quite large. The developers had to implement these systems in order to donate several documents in order to avoid re-ignition.

Fortunately, the new automatic gas fire extinguishing installations are free from the drawbacks of all their predecessors. Special chemical compositions allow the extinguishing agent not to remain on the surface of materials, but to penetrate into the smallest pores deep into the paper. Thus, smoldering documents are detected and eliminated at an early stage, and re-ignition does not occur. This is especially important for thick bundles of paper - for example, for bank vaults, since the fire loves to "get stuck" in the thickness of documents.
Conclusion
This article examined the basic automatic fire extinguishing installations and the principles of their operation. Also, criteria for one or another choice of fire systems were presented here. Remember that when choosing many options for fighting fire, focus on safety first and foremost. At the same time, it is important to consider both the safety of people and the safety of material values. One and the same type of installation can play a decisive role in extinguishing a fire in one case, and cause even greater material damage in another. The design of automatic fire extinguishing systems is a complex and responsible process that requires comprehensive comprehensive consideration.
Many facility managers are not serious about the issue of choosing equipment for fighting fire, believing that nothing like this will happen to them.
As a result, when a fire occurs, completely inappropriate substances are often used to eliminate it.
To avoid this, it is necessary to entrust the choice of installing fire extinguishing systems to professionals. Only they are able to correctly assess the specifics of an object and determine which type of equipment will be most suitable.
What is the installation data
This is a set of devices that are triggered if the critical values \u200b\u200bof temperature, smoke in the protected object are exceeded. Autonomous fire extinguishing installations are usually used to localize and eliminate the source of fire at the very beginning of its appearance.
 The use of such equipment is regulated by existing normative documents and recommended for both residential and public, industrial buildings.
The use of such equipment is regulated by existing normative documents and recommended for both residential and public, industrial buildings.
AUP Variety
The equipment used to eliminate the sources of ignition is structurally different. Depending on this parameter, it can be of the following types:
- Aggregate;
- Modular.
In addition, fire fighting installations are equipped with automation. Based on the presence of these elements, the equipment involves manual control or using automation systems.
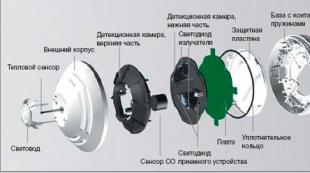
![]() Automatic fire extinguishing installations can work with various types of OM. Moreover, models are presented on the market that use either one of the means or several.
Automatic fire extinguishing installations can work with various types of OM. Moreover, models are presented on the market that use either one of the means or several.
Such a large number of means used to eliminate the fire has led to the emergence of various methods of fighting fire. Based on this, the following types are produced:
- Robotic fire extinguishing installations;
- Voluminous;
- Superficial;
- Local.
What are different kinds equipment where their use is allowed, what advantages do they have, the purpose of an automatic fire extinguishing installation? We begin the review with one of the simplest and most affordable substances - water. It is affordable and has a low cost.
Water models
Systems working with this extinguishing agent, have differences in the design of irrigators. They can be:
- Sprinkler
- Deluge.
The first are designed facilities on which there are materials with increased flammability. In them, the elimination of fires should be carried out simultaneously over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
Fire extinguishing systems can play the role of water curtains in cultural and public institutions, and are also suitable for extinguishing process equipment, containers with oil products. They perfectly cope with the creation of a water curtain.
Gas installations
This is a set of devices for eliminating fires, in which two groups of gases can be used as OM:
- Diluents such as nitrogen, argon;
- Inhibitors or chladones.
Using the first group of fire extinguishing substances are large in size and weight. While working with inhibitors is more compact, but at the same time, the concentration of gases in them is significantly lower and amounts to only 13% of 60% for the first group.
Not so long ago there were systems that use perfluoroketones. They are characterized by high environmental safety and can be used at any facilities, as they do not have a detrimental effect on objects and materials.
Watch a video about these systems:
Stationary gas fire extinguishing installations have differences in design and are divided into:
- Modular;
- Centralized.
Powder systems
Such installations have the widest scope. They are designed to eliminate foci of fire of any class, as well as electrical appliances that are in the on state.
Watch a video about this system:
Autonomous fire extinguishing installations for switchboards are used both for localization and elimination of fire sources in parts or all areas of a room. But at the same time, such settings can not be used on objects where they are stored:
- Combustible materials;
- Chemical mixtures that can smolder and burn without air.
Devices of this type are most often used at facilities where combustible liquids and rapidly flammable compositions, oil products are located. They are divided into deluge and sprinkler fire extinguishing systems and, in a constructive sense, are very similar to water installations. Their difference consists only in the presence of a tank. In this case, all components of the extinguishing agent are stored separately.
 For the dosage of OM in such installations can be used:
For the dosage of OM in such installations can be used:
- Pumps
- Dispensers;
- Foam mixers;
- Bucky
In addition, sprinklers or generators are used in foam systems.
Aerosol systems
In them, as a fire extinguishing agent, a special composition is used that can affect the focus of the fire. They are one of the oldest and were first used in 1819. In the first autonomous fire extinguishing systems, smoke powder, clay and water were used as the extinguishing agent. But over time, their use was suspended due to low efficiency.
Watch a video about this fire extinguishing system:
Modern stationary aerosol fire extinguishing installations cannot ensure the complete elimination of the fire source and therefore they cannot be used for:
- Fibrous and other materials with a tendency to spontaneous combustion or decay;
- Chemical compositions and polymers capable of burning without air;
- Metals, pyrophoric compounds.
As well as aerosols are harmful to human health, therefore, installations where they are used cannot be used in rooms that people cannot leave before the system starts working.
How to choose a fire extinguishing system
The most important criterion, which are guided in this case, are the features of the object. Based on them, a specific robotic fire extinguishing installation is selected. If it is intended to use equipment in buildings of public, warehouse, archival and cultural purposes, then immediately you can discard the use of foam as a fire extinguishing agent. In addition, it has recently been practically not used at any of the possible facilities.
Based on the features of the protected premises, you can formulate the main selection criteria:
- Efficiency;
- Safety for people;
- The inability to damage property.
Systems with solid extinguishing agents are most suitable for these criteria. It is possible to use water pumping fire extinguishing installations, since horses are safe for people. But at the same time, their property suffers very much. And if such a system works on the upper floor, then tons of water will fall on the lower ones, which will damage both material values \u200b\u200band the building itself.
Therefore, most often fire extinguishing pumping units are used with fine atomization systems, which minimize the impact on the environment.
Perhaps the use of gas SAPT. However, their use, especially with freon, is deadly to humans. Therefore, at facilities where people are present, they usually prefer a group of perfluoroketone gases. They are practically safe. But it should be borne in mind that the premises where the use of gas systems is supposed to be met are subject to strict requirements for tightness, and in addition, such equipment is quite expensive.
Maintenance and operation
 It is not enough to make the right choice, it is also necessary to complete the installation of equipment in accordance with existing requirements. After pipelines are completed and devices are installed with their connection to the mains, it is necessary to conduct tests. By the time of their implementation, it is necessary to evaluate the strength and density of all pipes, to check the quality of insulation of the wiring.
It is not enough to make the right choice, it is also necessary to complete the installation of equipment in accordance with existing requirements. After pipelines are completed and devices are installed with their connection to the mains, it is necessary to conduct tests. By the time of their implementation, it is necessary to evaluate the strength and density of all pipes, to check the quality of insulation of the wiring.
Testing a fire extinguishing pump installation consists of several stages. At the first, inspection of equipment, both technological and electrical. Then, autonomous tests of individual nodes of the system responsible for managing its operation are carried out.
External inspection also involves checking whether the placement of the devices corresponds to the design drawings. Autonomous tests are necessary to assess the correct interaction of all nodes and elements of the system. All work and commissioning are confirmed by the acceptance certificate. They must be accompanied by design drawings and other documentation.
Control devices and equipment that are part of fire extinguishing installations must have a certificate of conformity, meet the requirements of Russian Federation standards and regulatory technical documents, not have manufacturing and other defects.
Fire extinguishing installations must be operated in automatic mode.
The decision to transfer the automatic fire extinguishing installation to the manual start mode must be agreed with the local fire supervision authorities on the ground.
It is allowed to switch from automatic control to manual start only during the period of scheduled preventive or other work that is not related to the need to shut down the entire installation.
In the latter case, the facility manager is required to take measures for additional fire protection to compensate for the temporary absence of automatic fire fighting.
Elements and components of fire extinguishing installations should be painted in colors that meet the requirements of GOST:
- fire stop devices, manual start devices, start buttons - in red;
- pipelines filled with water in standby mode - in green;
-pipelines filled with air in standby mode- in blue;
-pipelines filled with water or air- in green and blue colors with alternating colored fields 2 meters wide;
- pipelines filled with carbon dioxide or nitrogen - in yellow, freon - in brown.
Fire extinguishing installations during commissioning after repair, partial or complete replacement of equipment must undergo 72-hour standby monitoring.
The premises of the pumping station, automatic water feeder and control units must have working emergency lighting, be constantly closed.
The keys to these rooms should be at the service (one set) and operational (duty) (second set) personnel.
In the premises protected by the automatic fire extinguishing installation, instructions should be posted on the actions of the personnel working in them in case of switching on the warning equipment, as well as in the case of an erroneous start-up or false (accidental) operation of the installation.
It is forbidden to turn off the automatic blocking of the supply and exhaust ventilation and technological equipment.
Cylinders and containers of fire extinguishing installations in case of excess of weight loss or decrease in pressure in them more than 10% are subject to recharge or recharge.
Water and foam fire extinguishing systems
In places where there is a risk of mechanical damage, sprinklers should be protected by reliable fences that do not affect the map of irrigation and heat flux distribution.
Wires and cables laid to sprinklers with remote electrical start-up must meet the requirements of the PUE.
Within each distribution pipeline (one section), sprinklers with outlet openings of the same diameter should be installed.
Sprinklers should be kept clean at all times.
During the repair work in the protected premises, irrigators should be protected from plaster, paint and whitewash.
After completion of the repair of the room, the protective devices must be removed.
The stock of sprinklers at the facility (enterprise) should be at least 10% for each type of sprinklers from the number of sprinklers mounted on distribution pipelines, for their timely replacement during operation.
Forbidden:
-Install instead of opened or faulty sprinklers, install plugs and plugs, as well as install sprinklers with a different (except for the design and estimate documentation) melting point of the lock;
- store materials at a distance of less than 0.6 meters from the sprinklers.
Pipelines in rooms with a chemically active or aggressive environment must be protected with acid-resistant paint.
Forbidden:
- the use of pipelines of fire extinguishing installations for suspension or fastening of any equipment; -connection of production equipment or sanitary equipment to the supply pipelines of the fire extinguishing installation;
-installation of valves and flange connections on the feed and distribution pipelines;
-use of internal fire hydrants installed on the splinker network for purposes other than extinguishing a fire; - the use of compressors is not for its intended purpose.
Each control unit must have a functional piping diagram, and on each direction a label indicating the operating pressures, the names of the protected premises, the type and number of sprinklers in each section of the system, the position (status) of the locking elements in standby mode.
Reservoirs for storing an untouchable supply of water for fire fighting should be equipped with devices that exclude water consumption for other needs.
At the enterprise for foam fire extinguishing installations, a 100% reserve stock of the foaming agent should be provided.
The room of the pumping station should be provided with telephone communication with the control room.
At the entrance to the premises of the pumping station, the sign “Fire extinguishing station” should be hung up, and a light board with a similar inscription should constantly function.
In the room of the pumping station, clearly and neatly executed piping diagrams of the pumping station and a schematic diagram of the fire extinguishing installation should be posted.
All indicating measuring instruments must have inscriptions on operating pressures and the permissible limits of their measurements.
At the control room (facility) must be around the clock duty personnel in an amount of at least 2 people.
The control room should be provided with direct telephone communication with the premises of the pumping station, main water supply, urban telephone communication, working electric lights (at least 3 pieces), as well as personal protective equipment.
A light and sound alarm should be provided in the control room about the operation of fire extinguishing installations, as well as about any malfunctions that arose in the system
In the control room should be posted instructions on the actions of the duty personnel upon receipt of signals about the operation of the installation.
Gas extinguishing installations
The requirements for the maintenance of nozzles and sprinklers, as well as pipelines of gas fire extinguishing installations, are similar to the requirements for water and foam fire extinguishing installations.
The gas fire extinguishing installation station during its operation in standby mode must be provided with a 100% reserve of extinguishing agent.
Each switchgear must have a sign indicating the name and location of the protected premises.
The premises of the fire extinguishing station must have first aid kits located in specially equipped cabinets, as well as insulating personal protective equipment (insulating gas masks).
The premises of the fire extinguishing station should be provided with direct telephone communication with the control room. At the entrance to the premises of the fire extinguishing station should be hung a sign and a permanently functioning sign “Fire extinguishing station”.
The premises of the fire extinguishing station should have clear and neatly executed piping schemes and a schematic diagram of the installation.
Air ducts must be provided with pressurized valves that close automatically when the fire extinguishing system is triggered, to prevent the extinguishing agent from entering the rooms adjacent to the protected one.
For persons working in a protected room, instructions should be developed on the procedure for their actions and evacuation upon receipt of a warning signal about the operation of the fire extinguishing installation.
The operation and maintenance of volumetric aerosol fire extinguishing systems of the CAT type should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of NPB 21-94, other applicable scientific and technical standards.
Premises for which volumetric fire extinguishing installations are provided should have hermetically sealed doors.
Manual start devices for volumetric fire extinguishing installations (except for local ones) are located outside the protected premises at the evacuation exits with free access to them.
Manual start devices for fire extinguishing installations, as well as manual fire detectors fire alarm must be provided with protection against damage, unauthorized putting them into action and sealed.
The requirements for control rooms are similar to the requirements for control rooms of water and foam fire extinguishing installations.
All indicating devices must have inscriptions on operating pressures, as well as on the operating position of valves, gate valves, etc.
Powder fire extinguishing installations (UPT)
The technical means of UPT must comply with design decisions, technical documentation of manufacturers and mark certificates of conformity.
The starter must have one of the following types of start-up, depending on the type of system:
-pneumatic;
cable (manual);
-electric;
-combined.
At food enterprises, automatic installations are used: water quenching —- sprinkler and deluge; steam, gas and powder fire extinguishing. The choice of a particular installation is carried out based on the properties of substances and materials formed in production, technological requirements and feasibility studies.
Automatic systems prevent or extinguish a fire in a timely manner. Without human intervention, they detect a fire and, after giving an alarm, begin to eliminate the fire in the initial stage of its development.
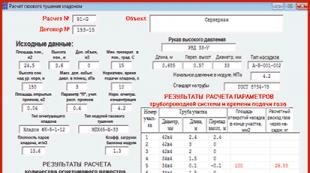
Circuit diagram automatic fire extinguishing installations are shown in fig. 61. When a fire occurs, the detector-detector 4 detects the place of sunbathing and notifies the system switching device 5, which, in turn, drives the extinguishing agent supply device 2 through the exhaust device 5, which eliminates the ignition.
Fig. 61. Schematic diagram of the installation of automatic fire extinguishing:
1 - apparatus for storing extinguishing agent; 2 - device for supplying a fire extinguishing agent; 3 - system enable device; 4 - device for fire detection and warning about it; 5 - device extinguishing agent; 6 - the center of burning
According to the principle of operation, automatic extinguishing systems are divided into devices designed to supply extinguishing agent evenly throughout the room. For this, sprayed water, foam or powder formulations are most often used. There are devices for filling the entire volume of the protected space with a fire extinguishing agent. In such cases, water vapor, carbon dioxide, inert gases are usually used. Local systems are also used to protect technological devices and equipment. To do this, use substances that inhibit the combustion process and powder compositions.
Sprinkler installations are designed to extinguish local (local) ignitions in certain areas of non-explosive rooms, and deluge installations are used to extinguish a fire throughout the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe premises, including hazardous explosions. The piping network of the sprinkler units is equipped with sprinkler heads (Fig. 62). Their outlet is normally closed by a valve 5, which is held by copper plates soldered by low-melting solder - lock 6. The locks are designed for a certain temperature (72, 93, 141, 182 ° С). When a fire occurs under the head, the warm air rising upward melts the solder, the plates open themselves, the valves are pushed out of the seat using a membrane, and the hole opens. Water from the hole enters the outlet and is sprayed in all directions in a radius of 1.5. ..2 m on the floor area under the sprinkler head. At the same time, several heads can be triggered, which provides intensive extinguishing of the fire. A distinctive feature of sprinkler installations is that their piping system is constantly filled with water or air under pressure. When you open the valve of one or more sprinkler heads, the pressure in the system drops, which is a signal to a special device to turn on the pumps.
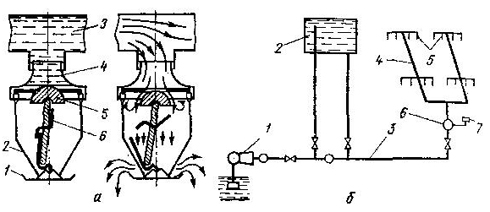
Fig. 62. Automatic fire extinguishing installation:
a - diagram of the sprinkler head in working and inoperative state (1 - socket; 2 - arc; 3 - valve; 4 - nozzles; 5 - supply pipe; 6 - fusible lock); b - sprinkler installation diagram (1 - centrifugal pump; 2 - water tank; 3 - main pipeline; 4 - supply pipelines; 5 - sprinkler head; 6 - control and alarm clan; 7 - signaling device)

Fig. 63. Extinguishing scheme;
1 - boiler room: 2 - technological pipelines, 3, 4 - valves; 6 - pipe for supplying steam; 7 - cranes; 8 - rubber hose
The piping system of the deluge unit is not normally filled with water, and the deluge heads have constantly open holes. In the event of a fire, the detectors give a signal to turn on the pumps, and water enters the room through all the deluge heads.
Drencher units are used in the same way as water protective curtains with remote or manual control, to protect openings (door, window, arranged for technological purposes), as well as to separate rooms in order to localize the fire source and prevent its spread to adjacent rooms.
At distilleries, premises for storing alcohol in tanks and at bakeries are equipped automatic installations steam extinguishing. In the extinguishing system (Fig. 63), both superheated and wet steam are used as extinguishing agent. The concentration of steam in the air is equal to 35% vol. and is considered extinguishing. The estimated time to create such a concentration is 3 minutes. The steam supply rate for rooms in which ventilation is provided is 0.005 kg / (s * m3). and for rooms or various technological devices in which air exchange does not occur, 0.002-0.003 kg / (s * m3).
The fire extinguishing system can only operate with steam boiler operation. In addition, the fire extinguishing system can be dangerous for people, since steam has a temperature of 160-180 ° C, so you can turn it on only by making sure that people leave the room.
A kind of automatic powder fire extinguishing systems is the local fire extinguishing system ASPGP (Fig. 64). When a signal is supplied from an automatic sensor detector 1 about the occurrence of a fire to the power supply and control unit 2, the limit switch 3 is turned on by a flame suppressor 4 - a pyro cartridge PP-9 and a gas-generating charge. The inert gases produced by the charge eject the powder through the nozzles into the fire 5 in the form of an atomized flame.

Fig. 64. Automatic system local fire extinguishing:
1 - sensor. 2 - power supply and controls; 3 - end switch; 4 - flame suppressor; 5 - fire
Automatic carbon dioxide liquid fire extinguishing systems are used to extinguish liquid and solid materials. Carbon dioxide can be stored at enterprises in isothermal tanks under pressure up to 2.5 MPa or in steel cylinders under pressure up to 7 MPa. Carbon dioxide is piped through a special nozzle to the protected volume of the building. When flowing out of a nozzle, the dioxide goes into an aerosol state (snowy mass), and then into a gas. Gas, spreading over the volume of the protected object, displaces the air, and combustion stops.
Carbon dioxide extinguishing concentration of 23%. but to stop burning it is brought up to 30%.