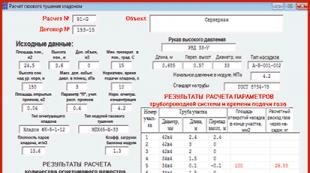
Check differential thermal fire sensor. Design features of the device. Device and scope of heat detectors
A thermal fire detector (TPI) is an automatic device for generating a fire signal, it responds to a given temperature value and / or parameters for increasing it. Sometimes the term “sensor” is used, but this is incorrect, since the sensor is only part of the detector.
In all countries, it has long become a tradition to use precisely thermal elements as basic detectors in automatic fire alarm systems. They are:
A dual alarm detector is a detector that uses two different types of detection. Dual detection technology is not the same as two different detectors in one enclosure. If one detector detects an intruder, the detector waits a moment to confirm this fact with a second detector. Both detectors should not work simultaneously. An alarm is triggered when a signal is generated by one of the detectors.
The higher efficiency and reliability of dual detectors can be explained in the following example. As you know, a passive infrared detector has the highest sensitivity in the direction perpendicular to the axis of the beam. In turn, the microwave detector is most sensitive to movement along the axis of the emitted radiation. The effect of this combination is to increase the sensitivity of the detector. In addition, in this regard, the probability of creating a false alarm is reduced by 100 times.
- have a simple design
- unpretentious in maintenance and
- cheap, which is important.
Thermal detectors use thermal sensors that operate on the well-known laws of physics. They work on the principles of changing linear dimensional parameters with temperature, the Curie law for ferromagnetic materials, temperature phase dependences of materials, temperature dependences of semiconductor resistance, and other laws. The first electric fire detector was thermal (the patent was obtained by Francis Upton and Fernando Dibble in the United States in 1890). When choosing the type of sensor for TPI, it should be remembered that its type depends mainly on the threshold temperatures of the responses, as well as on the inertia of these elements of the fire alarm.
Temperature sensors and other thermostats are also a very important element of smart buildings. A thermostat is a device that measures the temperature and maintains it at a temperature set by the user. The most popular methods of measuring temperature in building automation devices are the use of thermocouples or the use of thermistors. A thermocouple is a pair of wires of different metals and connected together. At the junction of these wires, a potential difference is created.
Thermocouples are characterized by high reliability, accuracy and design flexibility, which allows them to be used in various conditions. Thermoreversors are elements whose resistance changes in a measurable manner with a change in the ambient temperature. They are mainly made of metals such as platinum, nickel, copper. Types: radiator, room thermostats. The sensors are based on optical systems that respond to the diffusion of light through smoke. Optical sensors have advantages, but also disadvantages.
TPI are installed, first of all, in rooms where noticeable thermal radiation is emitted at the initial stages of ignition, for example, in fuel and lubricant warehouses. Often the use of other detectors is simply impossible or forbidden (for example, in office buildings in many countries). TPI is installed in the area of \u200b\u200bthe ceiling of the premises, since there is a zone of maximum temperature during a fire (usually the first tens of centimeters from the ceiling level).
The operating mode excludes their use in rooms, for example, in kitchens, where smoke may appear that is not the result of a fire. The great advantage of optical detectors is the rapid detection of smoke, which effectively protects fire in residential buildings. In the early stages of a fire, there is no rapid increase in temperature, so thermal sensors may not fulfill their role. As we said at the beginning, smoke and its toxic substances are the most common cause of death in fires.
The heart of ionization sensors is a slightly radioactive drug. The radiation causes a constant flow of ions between the two electrodes. At that moment when there is smoke in the detection chamber, the ion flow will be disrupted, which, in turn, will trigger an alarm. Ionization detectors have a very high sensitivity to gases from combustion.
Thermal fire detectors are divided into a number of types:
- point (react to fire factors in a small area);
- multipoint (represent a complex of point sensors placed discretely according to a linear principle, and their installation is regulated by the relevant standards, official documents and engineering and technical features that are indicated in the product documentation);
- linear (thermal cable).
In the latter case (linear TPI) there are a number of types that differ in design:
They respond to the heat released during combustion. Let's just add that optical heat gas sensors guarantee the most efficient fire alarm. It is individually programmed and adapted to the environment in which it works. The detector detects fires of fires and fires at an early stage, but recognizes and analyzes the parameters of smoke and heat. Based on these parameters, the optimal sensitivity and parameters are selected for each area that the detector monitors - thus, the detector is resistant to costly false alarms.
- semiconductor (the temperature sensor is a substance with a negative temperature coefficient covering the wire; for this type of TPI, an electronic control unit is required);
- mechanical (the temperature sensor is a sealed metal tube filled with a filled gas mixture, a differential pressure sensor and an electronic control unit; this type has a reusable effect);
- electromechanical (a type of linear thermal fire detector, a temperature sensor is a thermosensitive substance that is coated with a twisted pair, two conductors of which are short-circuited by thermal action after softening this substance).
According to the type of reaction to temperature, thermal fire detectors are divided into:
Fire alarm after smoke detection or temperature increase or after smoke detection and temperature increase. Alarm output for external alarm. Pre-alarm at 50% and at 75% threshold. 2-step recognition of pollution status.
Automatic threshold adjustment compensates for environmental impact. An alarm filter eliminates false alarms. Smoke analysis supported by temperature analysis function. Estimate the size of the fire using a software algorithm. Ability to detach individual detectors.
- maximum TPI, which are triggered simply when the desired ambient temperature is reached;
- differential TPI, which are triggered when the set value of the speed dynamics of the rise of thermal indicators in the room is exceeded;
- maximum differential TPI, which combine the functions and features of maximum and differential TPI.
According to physical principles, TPI actions are divided into the following categories:
The ability to read the total working time at the facility and the level of pollution. The detector detects background fires and is open at an early stage of development, detecting and developing fire characteristics based on the analysis of smoke and heat. The detector also has a dynamic alarm filter that recognizes and eliminates misleading alarms, as well as pre-alarm functions.
It should not be installed in production rooms. It combines an optical smoke detector with a heat detector. Both sensors have digital signals processed by digital processing, which leads to greater resistance to false alarms. The detector can be turned off for cigarette smoke or fireplace smoke. The optical sensor operates using the principle of diffusion of light and is very sensitive to the presence of large particles characteristic of dense vapors. The sensor is less sensitive to small particles, which are characteristic of "clean" images.
- using fusible materials that are destroyed by heat;
- using thermoelectromotive force;
- using the principle of the dependence of the electrical resistance of structural parts on the thermal factor;
- using thermal deformation of the material;
- using the dependence of magnetic induction on the thermal factor;
- finally, with any combination of the above principles.
To summarize. If you use TPI, you must know the principles of their work, characteristics, and for this, understand their data sheet, certificates of conformity. This will allow you to be sure of the possible results of their work in case of fire and fire. Our company provides the supply, installation and maintenance (including warranty) of all types of thermal fire detectors from leading manufacturers.
In particular, the smoke detector does not detect burning liquids such as alcohol. This deficiency is compensated by an integrated heat sensor. A heat sensor provides a slower response than a smoke sensor, but responds better to fast-growing smoke fires.
This can usually be done in most buildings. The acoustic power of the built-in siren. Diameter 126 mm, height 65 mm. This type of solution includes targeted fire detection and warning systems, as well as conventional systems. Modular and expandable firewalls interconnected over the network, capable of creating unlimited configurations, systems from dozens of detectors to several thousand. The proposed solutions are integrated with other common systems for controlled purposes.
The faster a fire is detected, the easier it is to extinguish and eliminate the consequences. On some types of objects, fire can spread rapidly and cause serious damage. Therefore, fire protection systems are installed everywhere. One of the elements in them are devices that recognize the onset of fires or smoke that are associated with the rest of the systems. In large rooms, production facilities, and warehouse farms, thermal fire detectors work efficiently. There are several types of devices and their principles of operation. There are also requirements of standards for their installation, manufacturing and characteristics.
Conventional fire detection and warning systems
If the detectors detect a set smoke or heat level, an alarm sounds. These types of detectors are connected to a circuit known as a “zone”, with each circuit connected to a control panel. If a normal detector enters an alarm state, the control panel will be able to determine which of the interconnected areas is the detector, but which of the detectors has detected smoke or heat.
Fire Detection and Fire Detection Systems
Intelligent detection and warning or addressing systems identify each sensor with a specific address. The fire control panel communicates with each device that reports heat or smoke levels, as well as control and management modules through which the system interacts with the rest of the building. The fire station, not the detector, decides to turn on the alarm state. Using an intelligent display and localization system for all elements of the system, the detected fire can be precisely located.
Application area
Thermal sensors are suitable for use in residential buildings, shopping and entertainment centers, workshops, outdoor areas. They are included in the fire alarm system. They are installed in areas where heat generation is possible in the event of a fire, while other detectors are ineffective.
Carbon monoxide detection systems
All carbon-containing materials provide a detectable level of carbon monoxide, the purpose of which is to detect these emissions in the early stages. These levels can be controlled to emit warning signals depending on the detected gas concentration.
Modular design with impeccable flexibility
It offers many advantages and innovations in the field of fire protection by reducing costs, increasing flexibility and raising reliability standards. Integrated interfaces that reduce costs. Connecting to the building integration system, along with other building safety and security systems, increases the efficiency of the system, maximizing the impact of the solution. Connecting stations to the network without adding additional modules makes investments more efficient. The system can be expanded to meet any specific needs. The modular structure provides an easy and economical installation. Expansion is facilitated by a modular structure that leverages existing resources. The downtime of the central components is eliminated: hot-swappable modules can be replaced without turning off the power. Linear temperature sensors are mainly used in areas where classic fire detectors cannot be used because of critical environmental conditions or when a large number of temperature sensors have to be installed, because of the very large areas that need to be monitored.
They cannot be used indoors where temperature changes occur regularly. This leads to frequent false alarms of the detectors. Mostly the simplest types of devices are installed in residential buildings, while thermal fire detectors are massively deployed at production facilities.
It is inappropriate to use in rooms where alkali is made and used, as well as there are radiation or crowds of people. The detector then either falsely triggers or its elements are destroyed.
Fire detection should be possible in all environmental conditions - not only in beautiful weather or at room temperature. Road and rail tunnels, surface or underground. Chemical industry. Bakery, bakery, food industry. Warehouses for liquid and solid fuels. 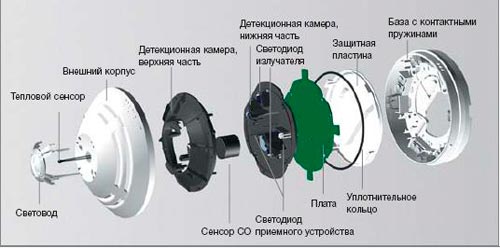
The sensor cable contains extremely sensitive and individually addressable temperature measuring points. The distance between the sensors is also freely adjustable. And the high resolution of the sensors allows extremely accurate measurements and estimates.
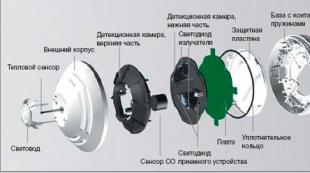
General principle of operation and design
 A primitive device consists of a controller to which a sensing element is connected. It is also called a thermal sensor. Data is transmitted from the controller via a loop to a common fire alarm control device.
A primitive device consists of a controller to which a sensing element is connected. It is also called a thermal sensor. Data is transmitted from the controller via a loop to a common fire alarm control device.
Thanks to electromagnetic protection, a fireproof outer casing and wear-resistant fittings, the cables are immune to interference sources and very stable. Due to its small size, the cable is easy to install along cable or conveyor belts and provides accurate alarms for the food, chemical and energy industries.
Thanks to electromagnetic protection, a fireproof outer casing and wear-resistant fittings, the cables are immune to interference sources and very stable. Due to its small size, the cable is easy to install along cable or conveyor belts and provides accurate alarms for the food, chemical and energy industries.
Modern detectors are equipped with other sensors. For example, carbon dioxide or smoke. Additionally, indicators are installed - LEDs that indicate which of the heat detectors in the fire alarm has tripped.
The sensitive element is of various designs and operating principles, but it must respond in one way or another to temperature changes. The limits are set depending on the characteristics of the sensitive element of a particular detector.
Detector Types
They are divided into types by type of sensitive element:
- contact;
- optical;
- mechanical;
- electronic.
According to the principle of action and response speed:
- maximum - trigger when the ambient temperature exceeds the set value;
- differential - respond to the rate of temperature rise above the limit;
- maximum differential - take into account both the excess of the temperature threshold and the rate of rise.
The classification of heat detectors according to the response temperature is also adopted, see the table. This is a standard separation, which indicates the ambient temperature and its limits for the norm or the operation of fire detectors.
The temperature of the heat detectors:
| Detector class | Ambient temperature, ° С | Operation temperature, ° С | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditionally normal | Maximum normal | Minimum | Maximum | |
| A1 | 25 | 50 | 54 | 65 |
| A2 | 25 | 50 | 54 | 70 |
| A3 * | 35 | 60 | 64 | 76 |
| B | 40 | 65 | 69 | 85 |
| C | 55 | 80 | 84 | 100 |
| D | 70 | 95 | 99 | 115 |
| E | 85 | 110 | 114 | 130 |
| F | 100 | 125 | 129 | 145 |
| G | 115 | 140 | 144 | 160 |
| N * | Indicated in the AP for detectors of specific types | |||
* Classes A3 and H are not available in ISO 7240 and EN 54-5
In residential buildings or small rooms, one-time detectors are often installed. In them, the sensitive element burns out and cannot be replaced. In other cases, they are unsuitable.
\u003e The measurement zone is divided into point, multipoint and linear devices. The former are appropriate for small control areas, while the latter are intended, as a rule, for workshops, warehouses, etc. In multi-point detectors, sensors are placed in loops that are distributed into zones according to the fire alarm design.
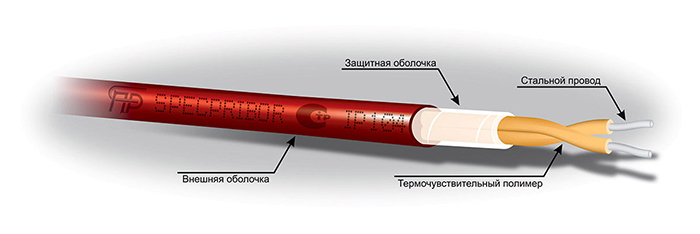
 Linear heat detectors are made in the form of a thermal cable - a cable of small cross section with a special coating applied to it. Under the influence of temperature, the resistance of the thermal cable section changes, which serves as a signal for warning of danger.
Linear heat detectors are made in the form of a thermal cable - a cable of small cross section with a special coating applied to it. Under the influence of temperature, the resistance of the thermal cable section changes, which serves as a signal for warning of danger.
Thus, the necessary protection of the premises is created in the form of a linear circuit, this cable is laid on the ceiling. It is convenient for large gas contamination of rooms, with a significant content of dust in the air and an increased fire hazard.
Cumulative heat detectors are formed when the distance between the point sensitive elements is less than the radius of their action. Simultaneous response to thermal effects significantly increases the efficiency of the devices.
Contact
Contact thermal fire detector assumes the presence of a steel conductor inside or several. They are coated with a special substance that responds to changes in temperature conditions. It should be fusible.
The heating of the sensitive element of the contact detector occurs due to the reaction of the coating when certain ambient temperatures are reached. A short circuit occurs, and control panels evaluate the resistance in this area.
Contact detectors are easy to operate and have a long service life. They are easy to install, they are practically not susceptible to dust, high humidity. However, their temperature ranges are not wide, so the choice of installation objects for them is limited. Compared to other types, inexpensive and reliable. Thermal sensors do not change to new ones.

Electronic
Electronic detectors have one of the most complex operating principles. The internal device consists of temperature sensors that are located in the cable. The distance between the sensors corresponds to certain values.
 Electronic heat detectors work with changes in electrical resistance. They are associated with an increase or decrease in ambient temperature. The controller processes the received data and transfers them to the control device of the common system.
Electronic heat detectors work with changes in electrical resistance. They are associated with an increase or decrease in ambient temperature. The controller processes the received data and transfers them to the control device of the common system.
Their advantages are low response delay and high sensitivity. Electronic detectors are extremely susceptible to electromagnetic interference, but in general do not require a special approach in installation, maintenance. They can work at a great distance from the control-receiving device (up to 2.5 km).
Optical
A central element in optical devices is fiber optic cable. Elevated ambient temperature leads to changes in its structure, and light from a special laser is reflected when it hits it. The optical detector controller determines the area where the temperature and its value have changed.
These devices operate at a great distance from the control-receiving device (up to 8 km). Optical heat detectors can be used in fire alarm systems in case of interference, risks of corrosion, high humidity, pollution and other potentially dangerous factors. Inertia is extremely low. The sensitive element must be replaced, its cost is low.
Mechanical
A key element in mechanical detectors is a thermocouple. Inside the metal tubes is compressed gas. When heated due to an increase in ambient temperature to a certain limit, the pressure that the electronic unit registers changes.
The design includes one of the many fire alarm sensors. Its task is to determine the change in pressure and transmit a signal about this to the control device.
Among the shortcomings of such detectors, a small distance to the electronic unit is noted\u003e. This is one of the reasons why they are practically no longer used in modern fire fighting systems. The sensing element in mechanical detectors is reusable. Despite the limited characteristics, they are still used on objects with specific parameters. Mostly where other detectors cannot work for many reasons.
The first detectors of this type were equipped with churches more than 200 years ago. The simple design consisted of a cord with a load. In a fire, the cord burned out, and the load hit the bell. His ringing alert residents about a dangerous situation.
Installation
There are certain rules for choosing the location and number of thermal detectors in a fire alarm system in a particular room. They are also installed in conjunction with detectors that determine other fire factors.
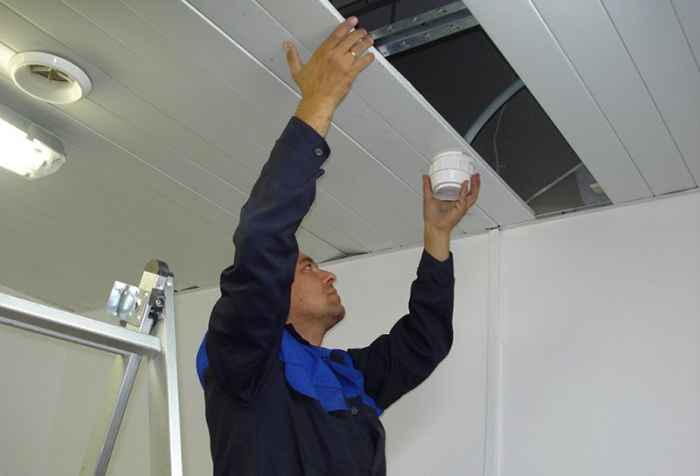 Thermal point detectors are placed mainly under floors, but other options are possible when this requirement is difficult to implement for technical reasons. Allowed their placement on the supporting structures.
Thermal point detectors are placed mainly under floors, but other options are possible when this requirement is difficult to implement for technical reasons. Allowed their placement on the supporting structures.
On the walls, point detectors are installed at a distance of 0.5 m from the corner and far from the ceilings. Also, the location of the detectors is affected by the parameters of the protected room - the ceiling height, the shape of the ceiling. All non-standard situations associated with installation require additional calculations according to current fire safety standards. All devices provide reliable mounts and stability. The choice of location is also affected by airflow from the sewage system.
Point detectors must be accessible for repair and maintenance, including when placed above 6 m.
You can not install a thermal thermal detector at a distance of less than 0.5 meters from fixtures and other objects. The location of such devices relative to each other depends on the data in the regulatory documents. The area of \u200b\u200bthe protected zone of the detectors is also indicated in the tables and depends on the type and design features. If the devices are combined, for example, thermal and smoke sensors are together, then they are counted as one unit.