The device and step-by-step installation of the truss system
The basis of a beautiful and reliable roof is a solid construction of the truss system. It is important to mount it in such a way that it will serve for many years, especially in difficult places of contact with the walls of the building, chimneys and pipes of the ventilation system. Depending on the weight of the snow, the wind load and the severity of the roof, it is necessary to choose the correct pitch of the rafters and the layout of the articulation nodes of the individual elements of the rafter group. We will consider options for attaching structural parts to floor beams and ridges, ways to increase the load capacity of rafter legs and step-by-step installation of trusses and a complex roof as a whole.
The device of the truss system
The construction of the roof is the final stage in the construction of the house, it determines the degree of protection of the building from atmospheric influences and the appearance of the entire building as a whole. The roof frame, on which the roof and insulation are mounted, is called the truss system. The device of the rafter group depends on the type of roof and its complexity, on climatic conditions and on the purpose of the attic. It is mounted on a Mauerlat, fixed on the walls of the house along the perimeter, and consists of the following elements:
- floor beam or puff - a horizontal beam based on a Mauerlat;
- hanging or layered rafter legs, which are attached at the bottom to a puff or Mauerlat, and at the top they are connected and form a ridge;
- run - a beam connecting the trusses of the truss group;
Depending on the type and size of the roof, truss systems are layered, hanging or combined, but their main elements are largely the same.
- racks, crossbars, struts and contractions are auxiliary elements that are necessary to give strength to the rafters and the entire roof structure;
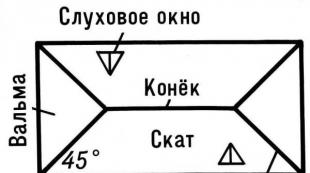
- sprigs - used on hip roofs and are shortened rafters;
The diagonal rafters of the hip roof are fastened with sprenels and trusses to ensure even distribution of the load.
- sprengels - designed to give strength to the diagonal rafters of the hip roof;
- filly - are used to lengthen the rafters and sprigs and form a cornice overhang;
- frontal boards - are attached to vertically cut rafters or filly and serve for mounting droppers, wind slats and brackets of the drainage system;
- counter-lattice - mounted on the rafters and used to create a ventilation gap between the waterproofing layer and the roofing material;
- crate - stuffed perpendicular to the counter-crate and serves to fasten the roofing material.
More complex types of roofs are formed from a combination of pitched, hipped and hip types, their truss system is also assembled from the described elements.
The basis of any system of rafters and trusses is a rigid triangular connection, which gives strength to the roof structure and allows it to withstand the weight of snow and wind.
Rafter device options
The rafter system of any kind is designed to create inclined pitched surfaces from which precipitation flows down without accumulating on the roof. In addition, the sloped surface better resists multidirectional wind loads. When installing a truss system, the following types of rafters can be used:

From these types of rafters, different types of roofs are assembled. Consider the most popular options for the device of pitched systems of various configurations.
Shed roofs are used in the construction of country houses, garages, baths and utility rooms. Such roofs are made using the simplest truss system, which can become more complicated with increasing slope length. If the distance between the walls of the building is more than 4.5 m, then the rafter legs are reinforced with struts. For spans of more than 6 m, it is necessary to use two rafter legs on each side or install an additional vertical stand with symmetrical slopes.
The choice of the design of a single-pitched truss system depends on the length of the slope, while the use of composite beams is allowed
As the length of the slope increases, the design of the truss system becomes more complicated with rigid triangular elements and contractions, which gives it additional strength.
Based on the experience of the author of this article, for soft roofing materials with small slope angles, it is necessary to use a solid plywood crate with a thickness of 12 mm or more. When sheet roofing material is used, the sheathing step should be reduced to 10 cm, the overlap should be increased to 15 cm, and the joints of the sheets should be additionally sealed.
Gable and broken attic structures
The gable type of roofs, traditional for the entire territory of our country, remains popular today. This is facilitated by the simplicity and reliability of the truss system, as well as the ability to equip a cold or inhabited attic. As a rule, a gable roof with an attic is formed by hanging rafters without an average support, and its rigidity is provided by crossbars and side posts, which serve as the walls and ceiling of the attic room.
Gable and broken mansard roofs are very popular in suburban construction due to the ability to equip an additional residential under-roof space.
Broken gable roofs are distinguished by the largest volume of the built-in attic, the frame system here is represented by a combination of hanging and layered rafters with different slope angles.
Gable rafter systems are characterized by simplicity of design, high strength and minimal consumption of building materials; such roofs are often used in budget summer cottage construction.
Four-pitched rafter systems
Four-pitched roofs are formed by two trapezoidal and two triangular slopes and have a complex structure of the truss system with a supporting frame, on which ordinary and diagonal beams are mounted. The space between the rafter joists is filled with spears, and the truss resting on the corner lintels serve as an additional support for the diagonal legs.
Four-slope truss systems are typical for hip and half-hip roofs, under which you can place a spacious attic room
Four-pitched roofs are perfectly protected from multidirectional gusts of wind and give the building a special chic, but their disadvantage is an expensive and difficult to install truss system.
The basis for the truss system of the half-hip roof is the walls of the building, on which the Mauerlat, girders and longitudinal trusses are located.
The truss group of a semi-hip roof, as a rule, rests on the side and front walls of the building and has a slightly different design with truncated triangular slopes.
The device of the supporting frame of hipped roofs
The rafters of hipped roofs in the upper part converge at one point and form a multifaceted pyramid. To increase the strength of the connection of the rafter legs, special docking elements, sheathing bars and additional sprigs are used.
The rafters of the tent system converge at the top at one point and are fastened together with ties, in the lower part they are fixed with cuts
Hipped roofs give the structure a unique look, but are characterized by an increased consumption of roofing and lumber. Most often they are used on outbuildings, gazebos, and in a truncated version - as bay window roofs.
Multi-gable truss groups
Multi-gable roofs are pitched fragments cut at right angles to each other and forming internal corners or valleys at the junction. The rafters of such a roof have different lengths, and the assembly of this structure requires professional skills, since the size and angle of inclination of the slopes may differ from each other.
The truss system of a multi-gable roof forms eight triangular slopes, at the junction of which there are valleys
Roofs of this type are designed to provide natural light to the under-roof space and have a very attractive appearance, but they are quite difficult to install and insulate.
The passage of ventilation and chimney pipes through the roof sometimes requires the displacement of the rafter legs with a violation of the selected step between them. But if there are pipes of sufficiently large dimensions, combined into one block, this is not enough. It is necessary to cut the rafters at the place where the pipes pass and connect the cut sections with other rafters with bars fixed to the corners. The distance between the pipe and the wooden elements must correspond to a fire gap of 130–150 mm.
The rafter system around the chimney is built taking into account the fire gap, and the cutout is reinforced with additional racks
Next, the trimmed rafters are fastened with the help of vertical racks to puffs or floor beams. Thus, a box is created around the pipe, which does not come into contact with its hot surface and, if necessary, is filled with non-combustible heat-insulating material.
Roofing over old roofing
In the process of service, the roofing is subject to natural wear and tear. If there is no deformation of the old truss system and you are convinced that it will last for a long time, then repairs can be made quickly and efficiently. When there is no time to dismantle the old roof, you can lay a new coating directly on top of the old roof. To do this, you need to know exactly where the truss beams with the counter-lattice and the batten boards pass.
According to personal opinion, drawn up on the basis of practical experience, for a new roofing it is better to choose corrugated board, metal tiles or ondulin, which will not create a large load on the structures of the old roof.
Video: roof replacement without dismantling the old one
The step of the rafter legs when installing the roof
When installing the roof, the rafters are installed at a certain distance from each other. This distance is called a step. Recommendations for choosing the pitch of the truss system are set out in SNiP II-26-76 * "Roofs". The decision must be made taking into account the following parameters:
- roof type;
- the length of the slopes and the angle of inclination;
- type of roofing material;
- section of rafters;
- expected wind and snow load.
The pitch and number of rafters can be selected based on recommendations and adjusted to suit the particular roof. For simple gable roofs with cold attics, the calculation can be made based on the following table.
Table: choice of length, pitch and section of rafters
Mansard and complex roofs require a more durable truss system with more frequent trusses and a change in pitch at butt sections with different types of slopes. On such roofs, a beam with a section of 50X150 and 100X200 mm serves as rafters, and the pitch is selected in the range from 60 to 120 cm.
In the construction of roofs with a habitable attic room, a beam of a larger section is selected, and rafters are installed more often to increase the strength of the truss
According to the observations of the author of this article, the dimensions of the insulation material have an indirect effect on the choice of step. For example, the standard width of the insulation is 60 cm, and the allowable pitch of the rafters with a section of 50X150 mm on a pitched roof is in the range from 60 to 120 cm. Prudent owners choose a step multiple of 59 cm in order to mount insulation mats tightly and without gaps between the rafters.
Complex roof construction
Complex roofs include multi-level architectural solutions, which are often characterized by a mixture of styles, for example, a pitched roof with a bay window or a combination of a hip structure with a tent element. Even an ordinary multi-gable roof with gables at different levels often has a very complex truss system. The design of such systems is carried out in accordance with the requirements of SP 64.13330.2011 "Wooden structures" and SP 17.13330.2011 "Roofs". Professional specialists should be involved in design work, since even a small mistake can lead to marriage and the loss of expensive materials.
Complex roofs should be built only according to ready-made design solutions that contain all the necessary information for the selection of materials and describe the sequence of installation work
The truss system of complex roofs can be divided into simpler components, and at their junctions, valleys, vertical racks and horizontal ridge-type beams can be mounted.
When installing complex truss systems, it is important to ensure that all slopes maintain a gap for under-roof ventilation, otherwise condensate will damage the rafters, battens and insulation layer.
Video: complex roofs
The nodes connecting the elements of the truss group perform the function of providing a rigid and durable fastening of parts. The assembly quality of the nodes is subject to increased requirements, since in these connections there is a uniform distribution of the load from the load-bearing elements to the puffs, floor beams and mauerlat. The main types of connections that are used during the installation of rafters include the following nodes:

There are also particularly complex connections, for example, the junction of the diagonal hip roof rafters to the purlin and the Mauerlat, or the sloping roof assembly, where five parts of the truss system are connected.
When assembling a sloping roof, special attention should be paid to the transition node of the hanging rafters to the layered ones, since five load-bearing elements are connected in them at once
Consider the attachment point for rafters, racks, girders and puffs using the example of a broken mansard roof. In it, the vertical stand is connected with a tie-in to a horizontal run and a puff, then the lower rafter leg is mounted to them, which rests on the puff with the help of a tie-in and a metal bracket. Then the upper truss truss is fastened with ridge ties and also cuts into the puff and is fixed on the bracket. In other nodes of the truss system, which are used on various types of roofs, the same principles for connecting parts are used. Nails, self-tapping screws, bolts, perforated metal strips and corners of various designs are used as fasteners.
Installation of the truss system
Before starting the construction of the truss system, it is necessary to carry out preparatory measures to ensure efficient and quick assembly. It is necessary to create a safe environment for work, prepare a place for cutting and making templates, as well as ensure the availability of lumber and fasteners. During the installation process, working drawings and the following tools will be required:
- goniometer (malka), level, construction pencil, cord;
- chain saw for rough cutting and trimming;
- circular saw, jigsaw;
- electric drill, screwdriver;
- hammer, chisels.
Before assembly, it is necessary to make templates of the same type of elements of the truss system and make sure that they fit well and fit well at the installation site.
Roof trusses must be made according to a single template, and this can be done both on the ground and directly at the work site
The final stage of the preparatory work is cutting the lumber to size, impregnating the elements with flame retardant and antiseptic compounds and natural drying for at least a day.
In the absence of project documentation for the roof, it is important to choose in advance the methods of fastening the rafter legs in the ridge and cornice parts, as well as design solutions for connecting parts in various docking and other nodes.
The rafters are fastened to the floor beams or puffs in the lower part in various ways, depending on the complexity of the truss and the length, and therefore the weight of the rafter legs. Rafters with a length of less than 4 m and a cross section of 50X100 mm are sufficient to be attached to the beams with a plank knot or using metal plates, cutting the timber at the required angle and using surfs.
The choice of the method of attaching the rafter legs to the Mauerlat or floor beams depends on the angle of inclination of the slopes, the weight and length of the rafters, as well as on the expected external load
With large values of the length and weight of the rafter legs and the expected snow and wind load, the connection must be made with a frontal cut, single or double tooth. In this case, sub-beam linings are used to ensure a snug fit of the threaded studs. Before installation, it is necessary to create templates that will ensure the correct cutting of materials at the cutting unit and the perfect fit of the elements. To avoid chipping at the edges of the floor beam, it is necessary to cut to a depth of at least 2 cm and at a distance of 1.5 h from the edge of the beam (where h is the height of the beam).
It is important that the holes for the threaded studs are located at an angle of 90 ° to the upper plane of the rafters, as this will ensure a snug fit and secure attachment of the parts to each other without displacement or distortion.
How to make cuts on truss beams
In the process of assembling the rafter system, it is necessary to join elements with different angles of inclination. Building levels and goniometric tools are used to mark cuts, cuts and corner joints, and templates are made in the mass production of the same type of parts. Washdowns on the rafters can be done in the following sequence.
- The timber is exposed to the Mauerlat and the ridge run, vertical lines and the exact position of the tie-in are marked according to the level.
- The angle of inclination is fixed on the bevel, and the dimensions of the insert are measured with a tape measure or square.
- With the help of a square and a goniometer, the measurement results are transferred to the workpieces, after which the cutting angles and the dimensions of the cutting spikes are marked.
- On the marked workpiece, the necessary cuts are made.
Places for cuts are marked in several stages using a construction pencil and goniometric tool
Diagonal rafters or sprigs come to the junction at different angles in two planes, in this case, using the level, the vertical angle of the junction is marked, and then the desired junction angle is fixed with a small one and transferred to the part.
According to the author of the article, cutting the material according to a single sample is not an unnecessary operation, since the time spent on making templates is more than paid off during the installation process, which is significantly accelerated and becomes more rational and of high quality. It is necessary to pay attention to the good condition of the goniometric tool and use only proven specimens.
Do-it-yourself installation of the truss system step by step
Many owners, in order to save money, mount the roof of the house on their own. With some building experience, this decision is quite justified, since even complex roofs can be assembled with your own hands, having project documentation. In the absence of a project, it is necessary to make a drawing of the future structure yourself with the main parameters and dimensions of the elements of the truss system.
Rafter truss blanks can be assembled on the ground or directly on the roof. Usually a triangle is made from two side beams and a lower puff, all other elements are mounted after the truss is in a vertical position. Each design must be made according to a template made in advance and tested at the installation site. With a significant length and weight of structural elements, assembly is carried out in stages.
Installation is carried out in the following sequence.
- On the threaded studs of the reinforced belt or the last crown of the walls around the perimeter, solid Mauerlat bars are mounted to ensure even distribution of the load from the rafter system to the walls of the building.
In the houses of their concrete or building blocks, the Mauerlat is installed on studs embedded in the armored belt; in wooden buildings, the last crown of the wall usually plays its role
- Floor beams or puffs are attached to the Mauerlat with brackets, metal corners or bolts. When using long and massive rafter legs, vertical racks are mounted in the middle of the floor beams, and ridge runs are attached to them.
- The first blank for the roof truss is installed from one edge of the roof (on the pediment). A tie-in is made on the rafter legs, and they are attached to the Mauerlat, floor beams and ridge run.
Roof trusses on the gables are installed first
- The second blank is installed in place of another pediment.
- Both farms are fixed in a vertical position, which is controlled by a level or plumb line.
- Guide cords are pulled between the installed trusses.
Guide cords are pulled between the truss trusses installed on the gables to control the correct position of the intermediate elements
- Intermediate truss structures are installed with the selected step. All of them should be aligned vertically and along the stretched cords.
- Ridge and additional horizontal runs are mounted (if they are provided for by the design).
- The rafters are reinforced with crossbars, racks and other elements provided for by the project.
After installing all roof trusses, horizontal girders and additional reinforcing elements are mounted
- On hip roofs, ordinary rafters are first installed, based on a ridge run and a mauerlat, and then diagonal rafters and rafters are alternately placed.
- With the help of gable and frontal boards, overhangs are formed that protect the walls of the building from precipitation.
- A waterproofing film with a sag of no more than 20 mm and bars of a counter-lattice are attached to the rafters, which provide a ventilation gap between the waterproofing and the roofing. Then a longitudinal crate is laid, which serves as the basis for the roofing.
Installation of a waterproofing film, counter-lattice and lathing completes the assembly of the truss system
Experience shows that with a rafter length of more than 6 m, it is necessary to build them up at the joints using a spike, double-sided pads and using threaded studs or bolts installed in increments of 15 to 20 cm. The joint must be reinforced with additional racks or struts. In 2010, using this technology, the author mounted a roof with a length of rafter legs of more than eight meters, so far no deflections or other changes in shape have been found on the slopes.
Complex roofs are mounted, starting with the main supporting structures on which the truss system is based. Then ordinary and diagonal rafter legs, sprigs and auxiliary elements are installed. In conclusion, different types of fragments are joined together into a single structure.
According to the author of this article, who mounted three roofs of varying complexity with his own hands, the installation of the truss system can and should be done by yourself. The first roof was cut and assembled according to the drawing in four days, and on the fifth and sixth day waterproofing, sheathing, frontal boards and roofing material were installed. The second roof took three and a half days, and the third was erected in two days. With the growth of skill and with proper planning of work, the installation of the truss system is significantly accelerated. If you have building experience, then installing a roof with proper quality is not difficult at all. In case of difficulties, it is necessary to involve design engineers or professional builders for advice, who will help in a difficult situation.
Video: device and installation of the truss system
We considered the options for assembling the truss system at the points of articulation with pipes, over old roofs, at the points of contact with the Mauerlat, as well as in the case of complex truss structures. Along the way, we studied some ways to connect elements of trusses and slopes. The roof can be assembled with your own hands, it is important to strictly follow the step-by-step instructions and strictly observe safety precautions, then success will be ensured.