Types of lighting lamps - an excursion into the variety of lighting equipment
Today, very often you can stumble across the Internet on materials telling about the variety of lamps, but none of the options seen by the author of the article can be called complete, and often the information provided does not correspond to reality. It is for this reason that we decided to publish an article about modern lighting lamps.
We will consider their classification, name the basic principles of functioning, not forgetting to point out individual advantages and disadvantages.
We will begin our list with well-known incandescent lamps that have faithfully served humanity for more than a hundred years.
An incandescent lamp is an artificial light source, which is emitted due to the strong heating of the incandescent body, which is most often a tungsten filament. The first models of such llamas had carbon threads, which served much less.
To avoid oxidation of the body of the heat from exposure to air, it is placed in a flask, which can be:
- Vacuum-sealed;
- Filled with halogen vapors (17th group of the periodic table);
- Filled with inert gases.
According to these features, the types of lamps are respectively distinguished: vacuum, halogen, gas (for example, krypton). They all have slightly different properties, which you will learn more about later.
Functioning principle
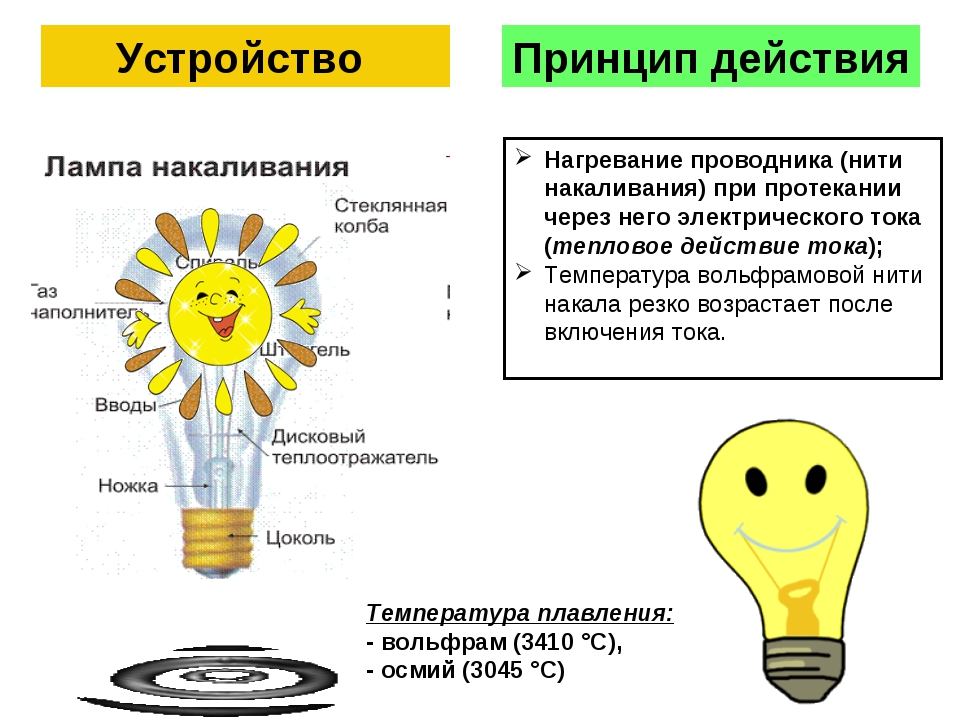
Heating of the incandescent body occurs due to the flow of electric current through it.
Advice! If you are interested in learning about the thermal effects of current, then check out the physical Joule-Lenz law.
As soon as the electrical circuit closes, an instantaneous rise in temperature occurs. We will not go deeply into the physical processes taking place in substances at this time, we will only say that in order to obtain a glow visible to the human eye, their temperature must exceed 570 ° C, which corresponds to the temperature of the red glow of the visible spectrum.

As you know, the most convenient for the physiological perception of a person is the glow spectrum, which emits an absolutely black body, the temperature of which will be equal to the heating of the surface of the photosphere of our Sun - 5770K. Unfortunately, science does not know substances that can withstand such heating without losing the original molecular structure, in other words, which will not melt.
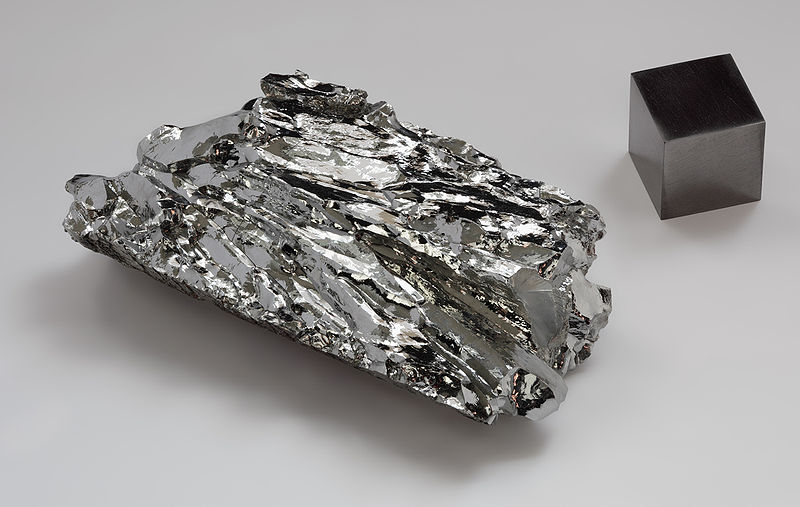

The temperature range in which the tungsten filament operates ranges from 2000 to 2800 ° C at a melting point of this metal of 3410 degrees. Less commonly, rhenium and osmium can be used as a heating body.
It is for this reason that the spectrum of light emitted by an incandescent lamp is shifted towards red, that is, it seems to us yellowish - the light of the sun becomes this way at sunrise and sunset. In this case, the main part of the spectrum is in the infrared range. We can immediately note the regularity that the lower the heating temperature of the emitting substance, the more red it appears to us.
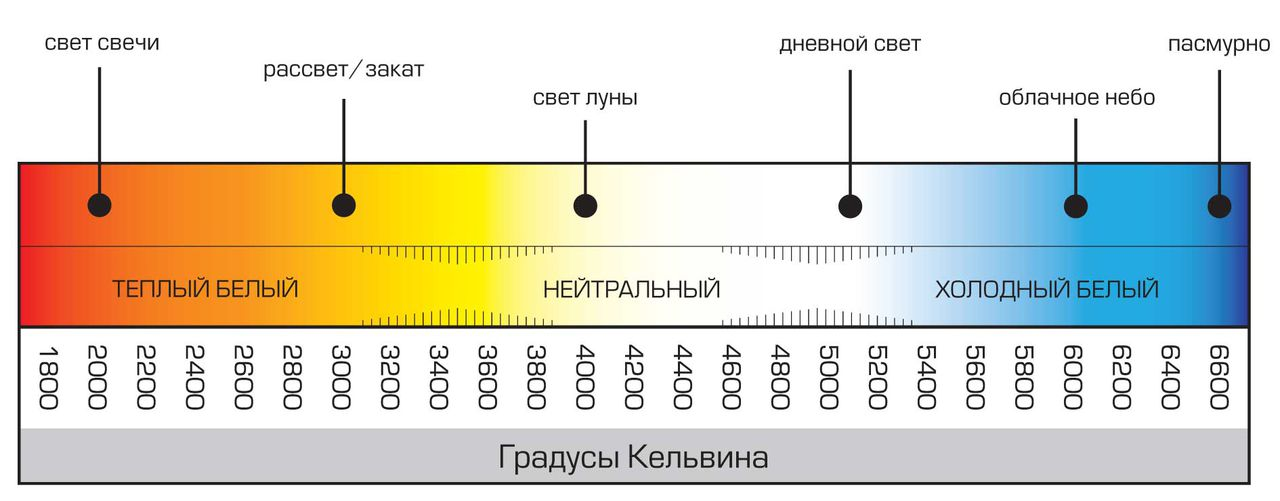
- For a better orientation in the visible color of light, they came up with a gradation in terms of color temperature, that is, each shade corresponds to a fixed value in degrees. Incandescent lamps operate in a color temperature from 2200 to 2900K, which corresponds to the yellow color scale. It differs from the natural daytime one, but it is very pleasant for us to perceive in the evenings, due to the fact that it does not disrupt the production of melatonin, a hormone responsible for the regulation of circadian rhythms.
- Upon contact with air, tungsten begins to actively oxidize, forming tungsten trioxide - a whitish coating on the lamp bulb when it loses its tightness. For this simple reason, the tungsten filament is placed in a sealed flask, from which air is evacuated, and an inert gas (krypton, argon or nitrogen) is pumped in for replacement under a certain pressure. Under these conditions, tungsten evaporates much more slowly, which means that the filament temperature can be increased, which also increases the service life.

- In turn, the luminescence spectrum is shifted towards white. The energy efficiency of the lamp increases - most of the radiation goes into the visible spectrum.
- At the dawn of incandescent lamps, the inner space of the bulb was under vacuum, but this design did not last long, due to its imperfection. Today, such lamps are only low-power (up to 25 W).
Pure metals, which include tungsten, and their alloys have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance. In simple words, this means that the more the metal is heated, the more it resists the current flowing through it.

Thanks to this feature, the incandescent lamp independently regulates the power consumption, that is, we can connect them directly to the electrical network without current limiting devices. This property favorably distinguishes incandescent lamps from fluorescent and LED lamps, which need drivers and ballasts, it is this feature that makes even the highest quality incandescent lamps many times cheaper than competitors.
Lamp structure
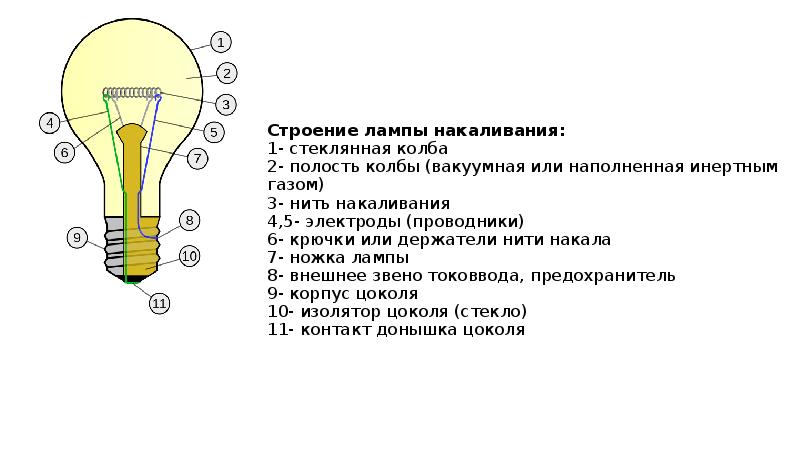
The structure of the lamp depends entirely on its type. Let's take a quick look at the general details of incandescent lamps:
- Flask- the main protection of the glowing body from atmospheric gases. Along the way, it can act as a diffuser. The size of the bulb is selected according to the deposition rate of the material from which the filament is made.
- Gas environment- so to speak, this is the internal atmosphere of the lamp, consisting, as already mentioned, of inert gases - most often of a mixture of argon and nitrogen, which is due to their low cost. This medium reduces heat loss, especially if gases with a high molar mass are injected. Separately, it is worth noting halogen lamps, which are supplemented with halogens and their compounds. The evaporated metal from the filament body, upon contact with them, returns back due to the thermal decomposition of the compounds formed. This property means a longer service life, which on average will be 2.5 times longer.
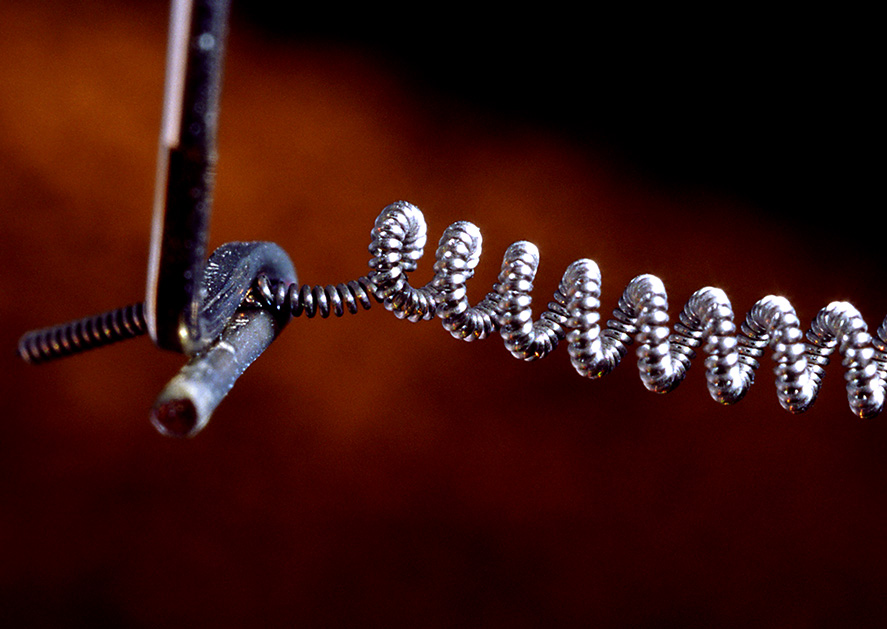

- Glow body- this element can be of different shapes and sizes, depending on the type and functionality of the lamp. Most often, you can find a round wire, twisted into a spiral to reduce the size, but there are also tape options. For this reason, electrical engineers replace the phrase "filament" with "filament" - this is the term included in the International Lighting Dictionary. Standard lamps have an incandescent body in the form of half a hexagon, which is made to evenly distribute the light flux.
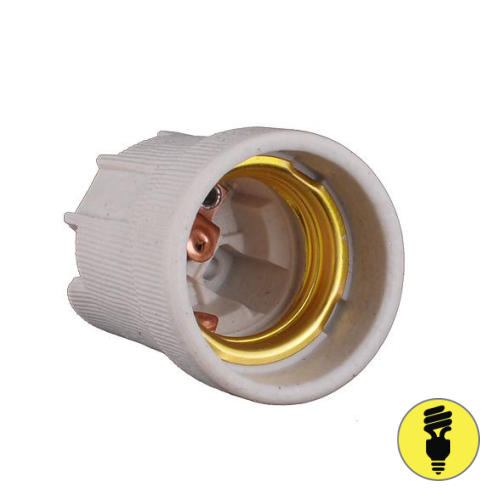

- Plinth- its shape is familiar to everyone. This is a threaded connection. The idea belongs to the English physicist and chemist Joseph Swan. The well-known Thomas Edison standardized the size of the base, proposing the variants E40, E27 and E14 that have survived to this day.

The thoughts of the author! Once again, we are convinced of how effective marketing works. Most of the inventions that are today attributed to Edison do not belong to him at all, and his merit is mainly the first mass production and the combination of purchased patents.
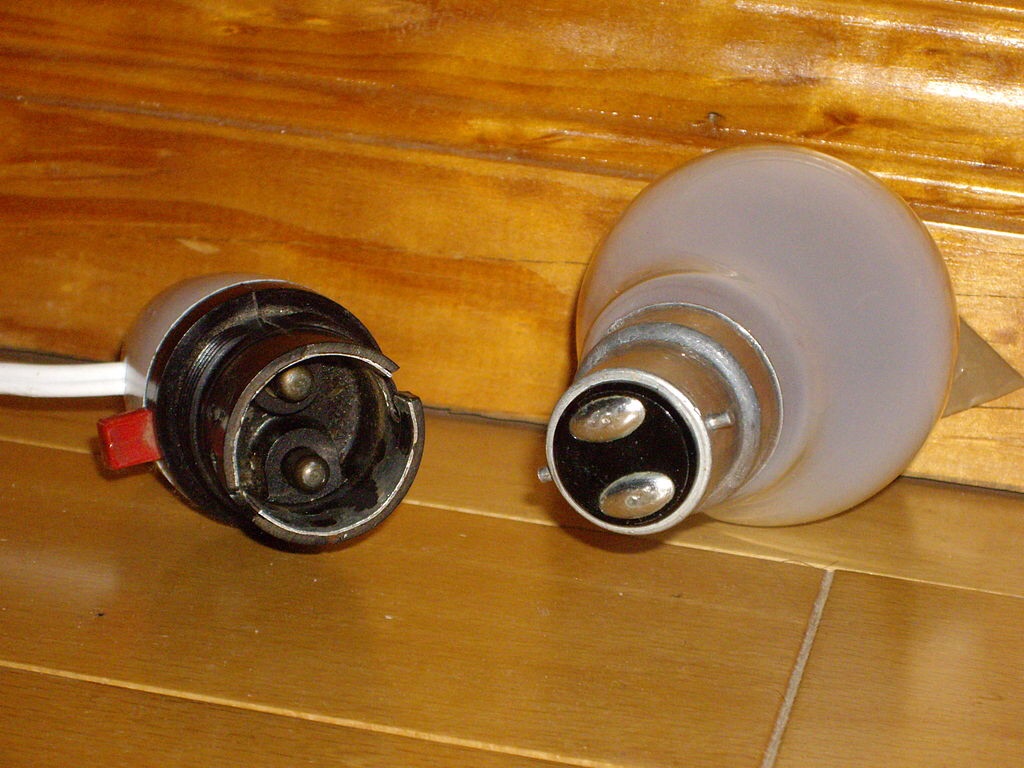

- There are other types of base, for example, bayonet which are very common in Britain. American caps differ from standard ones, due to the reduced voltage in public networks (110V) - this is done to prevent the possibility of screwing in European lamps.
Advantages and disadvantages

So, there are the following types of incandescent lamps:
- Vacuum;
- Argon or nitrogen-argon;

- Krypton;
- Xenon halogen with infrared reflector;
- With a coating that converts infrared radiation into visible - today serious developments are being carried out in this direction.
A person does not want to completely part with incandescent lamps due to their advantages over other light sources, but it is not possible to use them, as before, due to the modern trend towards energy saving.
Here are the advantages of these lamps:
- Finished product price;
- Compact dimensions;
- Immunity to power supply quality - voltage surges;
- Instant ignition and shutdown, which allows them to be used in dynamic lighting devices without any problems;
- The flickering of these lamps is imperceptible to our sight;
- Easy regulation of brightness by changing the voltage;
- Light spectrum pleasant for perception - it arises according to the same principle as sunlight; does not depend on third-party materials and is achieved only by the temperature of the emitter; has stability over time and is completely predictable; the glow is even and clean.

- Very high color rendering (100 Ra), which is irreplaceable when illuminating museums, aquariums and other things.
- Harsh shadows, again consistent with sunlight
- Lamps are not afraid of condensation and do not react to ambient temperatures;
- They can be designed for different voltages, up to hundreds of volts;
- Do not contain toxic substances;
- Unnecessary control gear;
- Ability to operate on AC and DC;
- There is no difference in the connected current polarity;
- The lamps are silent and do not cause radio interference;
- They are insensitive to ionizing radiation and electromagnetic pulses.
As you can see, there are a lot of advantages, but most of them are purely technical.
Let's now talk about the disadvantages:
- Short service life - 1000 hours, which is extremely short by today's standards;
Note from the author! There is a clear conviction that the data on the service life of different light sources are far-fetched, or established according to reference samples made from high-quality raw materials. For example, an ordinary incandescent lamp in your humble servant's bathroom has been continuously serving for 5 years, while halogen bulbs in rooms, with a seemingly long life (we put it, as expected, through a cloth) burn mercilessly. The same applies to energy-saving lamps, which, according to manufacturers' assurances, must work continuously for at least 2000 hours.
- Low efficiency;
- The dependence of the service life and luminosity on voltage;
- The release of a large amount of heat, and as a result - a high fire hazard;
- If the heating body burns out, the bulb may rupture;
- High requirements for heat resistance of materials for lamps;
- Glass bulbs are very fragile.
As you can imagine, the main disadvantages that force you to abandon these lamps are points 2 and 6.
Discharge lamps

The classification of lighting lamps continues. Next on the list are gas-discharge light sources that emit energy in the visible range.
The glow in the lamps occurs due to the appearance between the cathodes of an electric arc, similar to the one that we see when working with a welding machine. It arises with sufficient ionization of a substance in a gaseous state and the formation of a plasma.
Despite the fact that the principle of operation of such lamps is the same, it is customary to divide them according to the light source.
Fluorescent lamps

The first on this list are fluorescent light sources, the most classic of which is the standard tubular model used in factories and porches. Compact lamps, which people better know under the name "energy-saving", have also become quite widespread.
Visible light from such a source is formed when ultraviolet radiation passes through the phosphor layer, which covers the inner side of the bulb, and the radiation is excited by a gas discharge.
The interior space in such lamps is filled with inert gases and mercury vapors. At the ends of the bulb are tungsten electrodes, between which an arc discharge is continuously burning.
When an electrical discharge passes through such a medium, ultraviolet radiation is generated that the human eye cannot see. It is converted into visible light only when it passes through the phosphor, the composition of which determines both the glow color and its brightness.
The most commonly used phosphors are calcium-zinc orthophosphates or calcium halophosphates.

- The luminous efficiency of such sources is, on average, 2.5 times higher than that of an incandescent lamp. It serves for about five years, subject to the maximum number of inclusions equal to 2000, that is, no more than 5 times a day.
- They are widely used to illuminate various public buildings: hospitals, schools, offices and others - with their help, basic and emergency lighting is organized.
- After the appearance of lamps with a standard screw base and an electronic ballast, they became widespread in everyday life. In addition, they are often used for personal lighting of workplaces, illuminated advertisements and outdoor decorative lighting of buildings.

Unlike its predecessor, although it is probably wrong to say so, because the first gas-discharge lamps appeared back in 1856, that is, before modern incandescent lamps. However, this meant a competitor who had previously completely occupied a household niche.
So, unlike incandescent lamps, fluorescent light sources are more energy efficient, which is considered their main advantage.
Here are the other advantages of such a solution:

- A wide variety of light shades;
- Diffuse light that does not give harsh shadows, which is important, for example, when photographing;
- Long service life from 2000 to 20,000 hours - it is important to understand that this indicator depends entirely on the quality of the radio components used in ballasts and the quality of the phosphor. At the same time, fluorescent lamps need a good power supply. Therefore, if you want your lamp to last a long time, buy a quality product from manufacturers with a name.

The Dutch company "Phillips" is one of the leaders in the production of high-quality fluorescent lamps
However, fluorescent lamps, however, like all gas-discharge lamps, have recently begun to be very actively replaced by LED light sources, and there are plenty of reasons why they are losing ground:
- The most important is the chemical hazard due to the use of toxic mercury in the construction;
- The luminescence spectrum of the lamps is linear, uneven. It is unpleasant to the eye and can distort colors. There are lamps with a high color rendering index, but they, firstly, are expensive, and secondly, they cannot emit as actively as standard ones.
- During operation, the phosphor begins to degrade, which leads to a decrease in efficiency, deterioration of color rendering and a drop in luminescence brightness.

- The lamp has an unpleasant flicker that is noticeable to the human eye. The presence of sufficiently capacious capacitors in the electronic ballast can solve the problem, but manufacturers often save money by installing parts with insufficient capacitance.
- All gas-discharge light sources cannot be connected directly to the electrical network, which is why ballast control equipment is used, which cannot but affect the dimensions of the lamps and their cost.
- Fluorescent lamps create an unsuccessful load for the electrical circuit, which is also correctable in the presence of expensive electronic ballasts.
You can learn more about fluorescent lamps, including the history of their appearance, in one of the recently published articles on our website.
Gas lamps
These light sources are distinguished by the fact that it is not the phosphor that glows in them, but the gas itself. Neon lamps are a prime example.
They are started using the cold cathode technology, that is, it is not preheated due to the supplied current, but an emitter of free electrons is used. Such a start is harmful to the lamp, however, it can flare up instantly, unlike a hot start, where the lamp gradually increases brightness. During the operation of the lamp, the cathodes also reach a temperature, as with a hot start, but not immediately.
Lamps operating on this principle were previously used to illuminate LCD screens, today they are replaced by LEDs. Gas lamps are very economical, but they are not used for high-grade lighting.
Electric light lamps

This is the last gas-discharge light source. Electrodes glow in them, which are excited by a gas discharge. We will not go deep into the intricacies of these devices, since they are very close to those already mentioned.
General properties of gas-discharge light sources

- So, according to the magnitude of the pressure inside the flask, gas-discharge lamps are divided into models of high (ГРЛВД) and low (ГРЛНД) pressure.
- All of them have a very high light output, which means they consume less electricity.

- Different gases are used inside the lamps: metal vapors (sodium and mercury), neon, xenon and others, including various mixtures.
- The color temperature of the glow of the lamps can vary from 2200 to 20000K.
- For the operation of discharge light sources, starting devices are required.
Otherwise, we have already touched on everything and it's time to move on to the last type of lamps on our list.
LED lamp
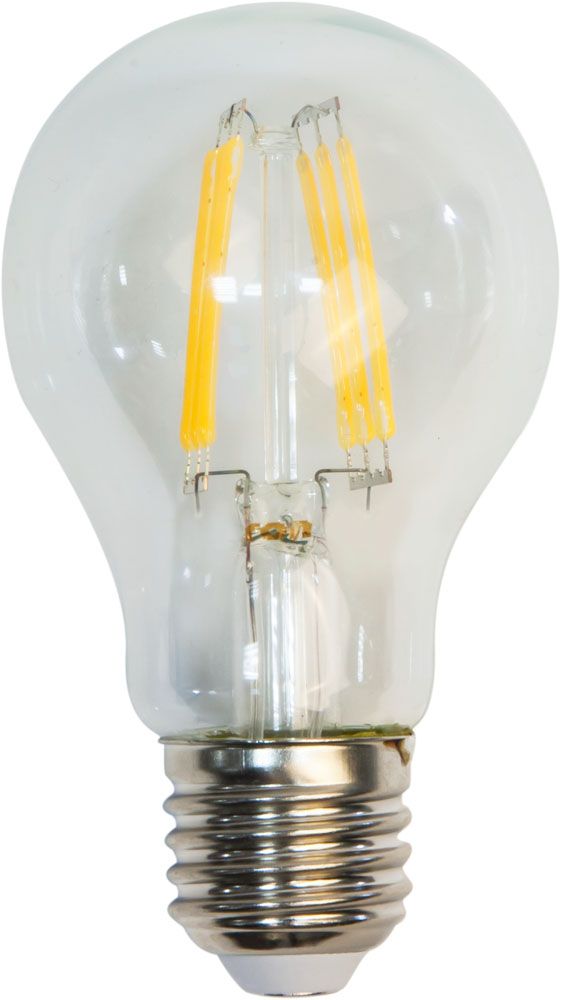

Inside each such lamp there are many LEDs, which are semiconductors of a certain type, when an electric current passes through them, light radiation is generated. They are used for both industrial and domestic lighting, being the most modern, economical and environmentally friendly light source.
Already today, LED lamps are becoming very widespread. They are actively used in consumer electronics for backlighting matrices of liquid crystal displays, which made it possible to make various devices more compact - phones with color screens appeared, followed by smartphones, tablets, ultra-thin TVs and much more.
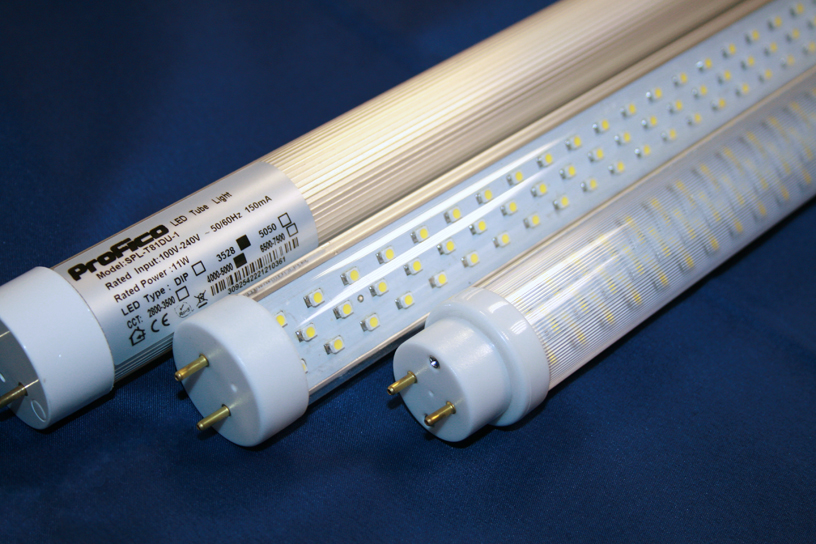

They are used for street lighting and crop production, in general, almost everywhere.
These lamps have the following advantages:
- Very low power consumption - they are more efficient than most discharge lamps;
- Long service life, independent of the number of on / off switching. It got to the point that manufacturers cannot give exact numbers, focusing only on the forecasts of special methods that give values from 30 to 70 thousand hours.
- Low heat generation, which allows them to be used near flammable substances.
- Significant mechanical strength - the lamp can easily survive even a fall from a height of a couple of meters.
- Environmental safety - the absence of mercury vapors, however, we immediately notice that many unscrupulous manufacturers do not hesitate to use toxic plastics, lead-containing solders and electrolytes.
- Sufficiently high color spectrum from 2700 to 6500 K, which allows you to create the right lighting for almost all household needs.
- LEDs are not inert and start immediately at maximum brightness.
- There are models of lamps with different glow angles.
- Insensitive to very low temperatures, while fluorescent lamps may not start at all.
- Hassle-free disposal.

Not without flaws, of which there are also quite a few:
- The first is the high price, especially when it comes to quality branded products.
- Many lamps shine in one direction and are not able to illuminate normally the surrounding space, which at certain points can be considered an advantage.
- Many manufacturers, especially Chinese, in pursuit of brightness and high efficiency do not pay due attention to the evenness of the glow - their lamps pulsate unpleasantly.
- LEDs are afraid of overheating. All the heat that they emit goes into the base, and if the manufacturer saved on the radiator, then do not expect the lamp to serve you for a long time.
- More often, the circuits use a serial connection of LEDs, which means that if at least one of them fails, the rest will stop working (like a garland).
- Be aware that the vast majority of LED lamps sold in Russia today do not meet the standards and norms that are established in its territory. The situation hasn't changed much since 2011.
- Many lamps sold do not have an accurate marking of all characteristics, which greatly complicates the selection of the correct lighting.

In the photo - LED panel for installation in ceilings
- Most white LEDs have a dip in the emitted spectrum around a wavelength of 480 nm. It is to this radiation that the human pupil reacts, narrowing when light hits. As a result, the retina can receive a dose of harmful blue radiation and vision can be impaired. However, some companies are already producing harmless LEDs.
- In general, the media often talk about the harmfulness of LEDs for vision. However, it should be understood that we are talking about a long look directed directly at the light source, which practically does not happen in everyday conditions.
Over time, LEDs lose their brightness, gradually fading out - everything in this world has a resource.
This concludes our story. We have covered all household lighting bulbs. If the topic seemed interesting to you, then you can read profile articles on our resource.