Independent construction of an underground greenhouse. Underground greenhouses Greenhouse from an old farm
An underground greenhouse is also called buried. It is these structures that are considered the best options for growing crops in a greenhouse. Such dugout greenhouses perfectly retain heat and are suitable for year-round gardening. No matter what the weather is outside, the ideal microclimate will remain inside. Thus, funds are significantly saved on laying a powerful heating system, as well as energy resources in the cold season.
Advantages and disadvantages of an underground greenhouse
You can make an in-depth greenhouse with your own hands, but before giving preference to such a design, you should carefully examine its pros and cons. Among the advantages, it can be noted that the construction and maintenance are within the power of both experienced gardeners and beginners in this business.

In addition, there are a number of other advantages that you should definitely pay attention to:
- In winter, inside the greenhouse, the temperature level does not drop below +10 ° C, and at the same time without additional heating. A winter greenhouse installed in the ground will perfectly preserve vegetables and plants in the best possible way.
- In summer, during the most intense heat, the plants will be closed from the scorching rays of the sun.
- In Russia, trench greenhouses are beginning to gain popularity, especially due to the fact that you can not spend much on purchasing materials.
- A buried greenhouse is the most ideal option for a greenhouse business all year round.
- At cost, such a structure is the most budgetary both in terms of building materials and finishing.
A thermos-type greenhouse functions due to a solid frame, foundation, as well as air space, which is formed under a film or transparent plastic.
Due to the fact that there is no draft, the air temperature remains stable.
The penetration of sunlight is carried out in sufficient quantities, and that is why in such structures the plants grow quickly and a large crop can be harvested.
Underground greenhouse for year-round gardening
Regardless of whether a greenhouse is used underground in Siberia or Ukraine, in order to grow crops in it all year round, it must be strengthened, insulated and provided with heating. On the inside, the walls should be covered with a layer of film, and not ordinary, but heat-insulating. If the region has too severe climatic conditions, then it is advisable to choose a foil thermal film. However, it needs to be mounted only before winter and removed in spring, as in summer it will create an additional greenhouse effect and heat, which will negatively affect the plants and their maturation.
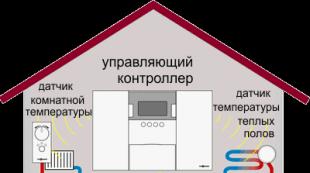
In order for the growing process to be as efficient and correct as possible, you need to install a certain battery that generates heat.
It is easy to make, because it is enough to use just plastic bottles with ordinary water. It heats up in a minimum amount of time and does not cool down for a long time. In addition, a barrel of water, underfloor heating with steam heating, a cable with electricity installed under a layer of soil can be used. In this case, the cable is poured with concrete and a special mesh is laid. Some gardeners prefer to cover the tiles, which allows you to make the greenhouse more beautiful and cozy. It is advisable to do the heating of greenhouses of a combined type, whereby both the soil and the air are heated at the same time. On average, the temperature will vary 25-32o C.
What material cover greenhouses underground
To build a greenhouse, you need to correctly select each material, including the coating.

There are paintings such as:
- Glass;
- Polyethylene;
- Polycarbonate.
It is polycarbonate sheets that are considered the most ideal material for such structures. Polycarbonate sheets in length reach 12 meters, which allows you to make a coating without numerous seams. The ventilation of the structure is minimal, since there are practically no joints, which eliminates the formation of drafts.
Additionally, to eliminate heat loss in a buried greenhouse, you can:
- Lay cellular polycarbonate doubly;
- Use thermal blocks for arranging a greenhouse along the upper edge of the soil;
- Wrap the walls inside the structure with a special thermal film.
As a rule, greenhouses are made either arched or gable with an acute angle, so that in winter the snow rolls off on its own, and also does not put pressure on the roof, which can cause its destruction and reduce its service life.
To increase the strength of the structure, it is worth using rafters, and it is from wood. Prior to installation, they are impregnated with a special compound to prevent the formation of rotting, insects and drying out, as well as to increase the service life. Between the rafters - supports, there should be a strapping with wooden bars. First, the rafters are installed along the length of the greenhouse, and then along the ends.
When building a structure, you can use not only wood racks, but also metal supports. They require special care, just like the rafters. Namely, the metal must be cleaned from corrosion, impregnated with a primer and painted. Basically, such procedures are carried out every year and are a natural service.
The installation of polycarbonate sheets is carried out by means of self-tapping screws, but through pre-drilled holes.
The end parts of the greenhouse are left unscrewed until the supports are completed and strengthened for the winter. Where polycarbonate is joined, a special sealant must be used, preferably frost-resistant, moisture-resistant and heat-resistant. It's not hard to find one at all.
Underground greenhouse cost
The greenhouse is deepened in order to significantly reduce the cost of building materials, as well as to increase the warmth inside the structure. It is worth noting that the price of a buried greenhouse is calculated only after the drawings, projects are drawn up, and there are also clear parameters and technical specifications.

In general, the price of a structure depends on a number of facts:
- What material will be used: improvised, expensive, cheap, high-quality or Chinese.
- From the method of attachment.
- From the thickness of polycarbonate sheets. It is worth considering the moment that if the greenhouse is winter, then polycarbonate needs twice as much.
The cost also depends on what area of the greenhouse will be built, because the larger it is, the more natural and more materials need to be purchased.
Materials and tools for creating a buried greenhouse
In order to equip a full-fledged greenhouse structure, in particular, a buried one, a standard set of tools and building and finishing materials is sufficient.
 The beginning of the construction of a greenhouse in the ground can be different. It depends on what you will use - improvised means or expensive materials from a hardware store.
The beginning of the construction of a greenhouse in the ground can be different. It depends on what you will use - improvised means or expensive materials from a hardware store.
We will need:
- Cement, ready or dry.
- Sand and gravel.
- Shovel shovel and bayonet type.
- A container, preferably roomy and made of wood, since the weight of the container with the solution will be large and additional kilograms are simply useless.
- Master OK.
- A mixture of plaster, preferably universal.
- Styrofoam in sheets.
- Thermoblocks of standard sizes.
- Polycarbonate sheets. Much better to buy long sheets. They bend perfectly and one cannot help but be afraid that they will burst or crack if strong supports are made.
- Film for thermal insulation.
- Construction tape.
- Nails are galvanized.
- Self-tapping screws.
- Hammer pliers.
- Primer.
- Dye.
- Brushes.
Underground greenhouses (video)
When forming an underground greenhouse with your own hands, you should pay special attention to the design, as well as the installation of supports not only for the roof, but also for walls dug in the ground. The depth must be sufficient. And the construction must be carried out correctly.
Ecologically clean greens, vegetables on the dining table are an essential addition to the diet with natural vitamins. If there is a land plot, they can be grown independently, using one of the types of buried greenhouses, in early spring, late autumn or year-round. This method allows you to get greens, vegetables with a minimum cost of heating the room. The design of the structure is selected depending on the region, time of use.
Types of structures
A natural phenomenon - the temperature difference between soil and air, the ability of soil to maintain temperature at a depth made it rational to use buried greenhouses in regions of the country suitable for these purposes. Almost all of them are designed for long-term use. After all, you have to dig a pit, since their effectiveness is possible at a depth of only twice the freezing of the soil. Depending on the location, type of wall materials, roof structure, buried greenhouses can be:
- Shed.
- Gable.
- Cylindrical.
- With brick.
- Wooden.
- Concrete.
- Dirt walls.

The structure can be up to 1.5 meters deep, and its above-ground part is one meter high. Compact buried greenhouses, in areas where soil freezing is negligible, can be built at no particular cost. This will allow you to grow greens, seedlings with minimal costs for space heating.
Gable earthen greenhouses with brick walls
Such designs are universal, suitable even for areas with fairly harsh climatic conditions. The capital structure will allow growing not only garden plants. It can also freely accommodate horticultural crops.
The construction of such a greenhouse is quite expensive. But the construction turns out to be convenient and in the future will become economical in use for many years. When erecting such a greenhouse, the following premises are provided:
- Tambour.
- Storage area for materials and supplies.
- Work zone.
- Greenhouse.
With year-round use of the greenhouse, it will have to install a boiler for heating. To do this, use the vestibule room. The reduction in heating costs is achieved by carrying out thermal insulation work, a heat insulator is placed between the walls and the ground.
Shed structures with wooden walls
This construction option is more economical than greenhouses with a gable roof. The frame of the building consists of three rows of wooden posts placed in the pit. On the north side, the first row is 20 cm below the average and is upholstered with a croaker. Eighty centimeters from it there is a middle row, sheathed to the height of the ridge. In the resulting notch, I have biofuel sprinkled with earth (10-15 cm). Above these racks, a roof is built into the cavity of which sawdust is poured. 
Racks from the south are made 30 cm above ground level, completely upholstered with croaker. On both sides, the walls are sprinkled with earth. On the north side, they also cover the roof covered with tar paper with it. In the working area, a chimney is built on the floor. And above it, a flooring is laid, on which racks with earth are placed, leaving space for free access to them. Such a greenhouse can be used all year round. In the absence of heating, it can be operated from the first months of spring until the onset of frost.
Features of greenhouses buried in the soil
- The use of a natural phenomenon, the preservation of positive temperatures by the soil below the level of its freezing, reduces the cost of heating such structures in the winter.
- The construction of such greenhouses will require digging a foundation pit to a depth of two large freezing soils in the location area. In colder climates, it is necessary to increase it. This leads to an increase in the cost of work.
- When constructing greenhouse structures, groundwater is taken into account. They must be located at considerable depths so as not to flood the greenhouse. For the functioning of the greenhouse, you need to take care of arranging a good drainage system.
- In places with a warm climate, optimal soils, unheated buried greenhouses can be built without strengthening the walls. It is enough to perform them with a slope opposite from the pit.
- Buried greenhouses are very effective in areas with a short summer period. They allow you to grow seedlings, get a full crop of vegetables, herbs.
Minuses
- Winter options for greenhouses require capital construction. And this is a significant cash outlay, and not everyone can afford it.
- You can place the building not in any place. Buried greenhouses are built only on suitable soils. The presence of groundwater, quicksand and other features of the soil makes their construction impractical.
- It is necessary to equip a high-quality drainage system around the building to prevent flooding from precipitation. And these are additional costs.
- The need to create a high-quality ventilation system.
- In areas with a shallow depth of soil freezing, the construction of such a greenhouse does not require significant investments.
- An economical option for heating in the winter.
- Can function in all weather conditions.
- They allow growing heat-loving vegetables, horticultural crops, flowers in regions with cold climatic conditions. Even exotic plants grow in them.
- The structure will last for many years.
- Effective for year-round industrial cultivation of seedlings, flowers, herbs, vegetables.
- Buried greenhouses allow you to get a full crop in a short summer.
Recently, the popularity of this type of greenhouses is growing. They can not only be equipped on personal plots to provide vitamins for the whole family. This is a profitable type of business for those who want to do business. After all, buried greenhouses significantly reduce the cost of their heating.
The soil tends to maintain a constant temperature - for example, if in the air it is close to 0 ° C, then in the soil, approximately (+ 10 ° C). This natural phenomenon is often used to build greenhouses that are sunken into the ground, which are called earthen or buried. Further, issues related to the features of earthen greenhouses, with the stages of their construction are considered.
The peculiarity of the buildings is the depth in the ground up to 1.5 meters, and the height of its above-ground part is one meter. A compact greenhouse, deepened into the ground, located in areas with little freezing of the soil, is built without much cost. Here it will be possible to grow greens, seedlings with minimal costs for space heating. Almost all such structures serve for many years of use.
Depending on the area where the greenhouse is located, the type of materials for building walls, the structure of the roof, buried greenhouses are:
- Roof shape:
- lean-to;

- gable;

- cylindrical.

- By wall material:
- brick;

- concrete;

- wooden.

- With earth walls.

Greenhouse Features
The simplest type of in-depth greenhouse is a rectangular shape, with a film (see) or plastic as a coating.

This insulated air space provides an ideal microclimate. Recessed greenhouses are quite easy to make with your own hands, and the sun's rays penetrating deep into the greenhouse create an optimal microclimate that favorably affects plants.
The table shows the pros and cons of greenhouses deepened into the ground:
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
Choice of construction site
When choosing a place to build a greenhouse, it is necessary to take into account the following main points:
- Wind direction. With the predominance of gusty cold winds in the zone, additional protection of the structure should be performed. Despite such costs, in the future there will be savings on heating. A fence can be used as additional protection.

Tip: You can not place an additional fence very close to the greenhouse. With a ridge height of, for example, 2.5 meters, the distance to the fence from the greenhouse should not be less than 8 meters. This is due to the fact that the wind flow that has come across an obstacle will go up and cool the structure.
- Light. It is very important that the greenhouse has the maximum amount of light during the entire daylight hours. This is essential for efficient crop growth.
- Accessibility to the building. When building a greenhouse for long-term and permanent operation, it is necessary to provide a convenient entrance to it.
Greenhouse construction
To properly equip a full-fledged greenhouse structure with a recessed structure, you should use a standard set of construction tools and materials:
- cement mortar.
- When replacing the mortar with cement, additional sand is required.
- Shovels - shovel and bayonet.
- Capacity for diluting the composition.
- Master OK.
- Mixture for plaster.
- Styrofoam sheets.
- Standard thermoblocks.
- Polycarbonate sheets or polyethylene film.
- Construction tape.
- Film, for thermal insulation of the structure.
- Impregnation, for protection of wooden lumber.
- Fasteners galvanized: nails and self-tapping screws.
- Pliers.
- Hammer.
- Paint, for coloring a framework from a tree.
Tip: When arranging an underground greenhouse, it is necessary to properly perform the waterproofing and drainage systems, and ventilation.
Installation steps
Before proceeding with the work, you should carefully watch the video in this article. The construction of a greenhouse structure begins with careful measurements of the area, and then the work is carried out according to the planned plan and developed drawings.
The instruction for the construction of the structure suggests that the construction be carried out in the following sequence:
- A place is chosen for the location of the building.
- The location of the building is marked according to the dimensions indicated on the drawings and the plan.
The standard width of the structure is no more than five meters.
- Dig trenches or pits according to the markup.
The foundation is being poured. To do this, the perimeter is laid out in blocks and poured with concrete or cement mortar.
- After the concrete has dried, the formwork is removed.
- The walls of the structure are erected from a material that has positive thermal insulation characteristics.
The preferred option for walls is the use of hollow polystyrene-based thermoblocks.
Tip: When laying walls, they should be reinforced with vertical metal elements. In this case, deepened greenhouses into the ground will acquire greater strength.
- Walls are being insulated.
To do this, the joints between the blocks are carefully smeared with a high-quality waterproofing solution, and all cavities are filled with a special mounting foam. To get the maximum insulation effect, it is necessary to attach a foil thermal insulation film on the inside of the wall.
- In order to heat the greenhouse all year round, it is advisable to arrange warm floors under the screed in it, to make artificial lighting.
- The roof frame is being built.
Construction of a shed greenhouse
To reduce the cost of an in-depth structure, you can use the budget option for its construction. In this case, the frame is made of wooden racks in three rows, as in the photo.
Construction order:
- The pit is digging.
- Racks are installed. Wherein:
- at the northern wall there are pillars, the length of which is 1.5 meters;
- in the middle row of racks 1.7 meters long;
- from the south wall - 0.9 meters.
- The extreme rows of racks along the entire length are sheathed with slabs, and in the middle row, sheathing with slabs is performed to the height of the ridge. This forms a notch with a depth of 0.9 meters, which is filled with biofuel for 0.7 meters, and a layer of earth is poured on top, up to 15 centimeters thick.
- The walls located on the north and south sides are sprinkled with earth.
- The slope of the roof, directed to the south, is covered with greenhouse frames.
Tip: To prevent heat loss through the roof, it is necessary to throw mats on the glass at night. They can be made of reeds, straw, film or even paper.
Greenhouses recessed into the ground are structures whose feature is the use of soil as a natural insulation. This significantly saves money on heating the greenhouse. Such greenhouses are very popular among amateur gardeners and professionals.
At different latitudes, we have different surface air temperatures, but the air temperature at a depth of 1.5-2.5 m remains unchanged at 10-15 degrees. Your greenhouse will perform better the deeper you plant it in the ground.

This is an underground greenhouse in Spetchley Gardens, UK. The entrance is visible on the right

Underground, raw brick (adobe) or any other dense natural material that can absorb a large amount of heat. Cold weather resistant crops such as lettuce, cabbage and broccoli can be grown here. Glazing creates a "greenhouse effect". You are unlikely to be able to build such a greenhouse if you have a high groundwater level. Such a greenhouse can be built at least 1.5 m above the groundwater level.

This is how Mike Ohler's underground greenhouse works. Mike digs a trench on the south side, which allows the cold air to sink down and warm up in the warm soil. Many install pipes in the ground to transfer heated air to the ground.

This is a diagram of an underground greenhouse made of bags filled with earth. The bags store heat during the day to release at night. A properly designed underground greenhouse naturally heats up on five sides, unlike an above ground greenhouse where only one side, the floor, heats up during the day. A waterproof barrier should be made along the walls of such a greenhouse www.naturalbuildingblog.com.

Another representation of underground greenhouses by Barbara and Ken Kern.
Here is a large walipini greenhouse from an organic farm in the province of Lapaz, Bolivia. Apparently they don't get much rain here.

This greenhouse is made from local stone in Nepal at nearly 3,000 meters above sea level, where temperatures drop below freezing 199 days a year. Lush vegetation inside: www.rids-nepal.org

This underground greenhouse is made in Mongolia and produces food during three seasons of the year. As the tracks show, the entrance is on the opposite side. thegreenbackpack.blogspot.com

Inside view. In cold climates, the north, east and west walls should be well insulated. In the north, the ceiling should also be well insulated. thegreenbackpack.blogspot.com

This underground greenhouse hole was dug in Texas. here it is solid and is not strengthened by anything. taroandti.com

This is an earth greenhouse in Patagonia. The bags form the walls, and the film goes much further behind them protecting from moisture. ourlittlething.ning.com

You can dig a shallow drainage ditch around the perimeter of the greenhouse to drain rainwater. darfieldearthship.com

Sometimes rainwater tanks are placed in the back of the greenhouse to store more heat. Pay attention to the vestibule for the entrance on the right. greenhouseglimpses.blogspot.com

This valpini greenhouse is made from old windows. onepinkhippie.com

This sunken greenhouse is hand-dug in New Mexico. Step by step photos: coatinativesnursery.com

Walipini greenhouse in Ladakh, lined with mud bricks, produces food all year round in a very harsh climate. More photos: ashdenawards.blogspot.com

Care must be taken when waterproofing, draining and ventilating the underground greenhouse. The most efficient underground greenhouses have windows to the south and a wall to the north to keep the heat in. In this greenhouse, a well was drilled for irrigation, it does not freeze.

This amazing couple bought an old swimming pool and turned it into an "urban greenhouse. They raise chickens and vegetables and fruits. Watch the video here: gardenpool.org

This clay greenhouse is made in Poland. A lot of natural clay absorbs heat. www.organica.net.pl
The 2 Most Important Factors When Designing an Underground Greenhouse
- a large amount of thermal mass (stone, soil, water),
- positioning towards the sun.

The easiest way to warm up and bring light to the basement. Build an underground mini-greenhouse on the south side of your house. naturalbuildingblog.com

Underground greenhouse used as dining room www.solarinnovations.com

And if the greenhouse has good acoustics, then you can make a studio www.imrevolting.net

This is the underground greenhouse of the New AIchemy Institute. There is a pond, a greenhouse and a house nearby. Water is dense and holds heat even better than rock, soil is third in heat storage. .
community.theaquaponicsource.com

Underground greenhouse at an organic farm in Wisconsin. The larger your greenhouse, the more efficient it is, as the temperature inside a small greenhouse can fluctuate quite quickly. More about the project.
The underground greenhouse is known to few. Modern gardeners annually seek new methods and technologies that are different from traditional ones. Summer residents who live in cold climates are trying to use the most unusual approaches that help extend the growing season and reduce the cost of building materials and heating. The category of rather interesting developments in this direction includes the option of the so-called underground or buried greenhouse structures.
Features of the building
Buried greenhouses are among the best and most rational options in the field of capital greenhouse structures and are considered to be very promising. Such a greenhouse-dugout perfectly corresponds to the idea of thermal preservation, which, thanks to optimal depth indicators, is stable throughout the year.
The use of such a thermal factor when constructing a greenhouse in the ground contributes to huge savings in heating costs during the cold season. In addition, structures of this type compare favorably with structures of a similar purpose by their ease of construction with their own hands, ease of maintenance and a stable microclimate, which is most significant for the growth and fruiting of crops.
Most popular options
The most popular alternative for expensive and energy-intensive glass greenhouses is the underground greenhouse "Walipini", which came to us from the Indians inhabiting the cold mountainous regions of South America. The Walipini greenhouse facility uses natural resources to provide stable heat and quality lighting all year round.

The simplest type of greenhouse located in the ground is a rectangular recess, in which plastic or film is used as a covering. The insulated air space created under such a coating contributes to the formation of an ideal microclimate. Such buried greenhouses are quite easy to do with your own hands, and the sun's rays, penetrating deep into the greenhouse, favorably affect garden crops. Greenhouses buried in the ground consume much less energy compared to ground-based greenhouse structures. The most effective models are underground greenhouses with a length of six meters, equipped with plastic wrap and PVC pipes.
Main advantages
Greenhouses, buried to a sufficient depth, have some advantages, which makes them in demand not only among experienced summer residents, but also for beginners:
- in winter, temperature indicators can be more than ten degrees, provided that there is no additional heating of the greenhouse space;
- on hot summer days, most plants need coolness, which freely occurs in this type of greenhouse underground;
- it is absolutely easy to make a construction with your own hands, and classic schemes and drawings for construction are more than available;
- trench greenhouses are ideal for year-round cultivation of not only vegetables, but also many berry crops;
- the low cost of construction is due to the ability to use an affordable and budget option for building and finishing materials.

Thermos greenhouse: recessed structure (video)
Necessary materials and tools
To equip a full-fledged, which is a recessed structure, you should use a standard set of building materials and tools for performing this kind of work:
- ready-mixed cement or cement;
- when replacing the cement mixture with cement, sand should be used;
- shovel and bayonet shovels;
- a container or any convenient container for diluting the working solution;
- construction trowel;
- plaster mixture;
- sheet foam;
- standard thermoblocks;
- sheet polycarbonate or high-quality polyethylene film;
- film for thermal insulation works and construction tape;
- protective impregnating composition for wood lumber;
- galvanized nails and screws;
- hammer and pliers;
- wood frame paint.

Installation steps
When performing a recessed greenhouse structure with your own hands, you should carefully take all measurements and carry out all work in accordance with the planned plan and completed drawings. The standard design is built in several successive stages.
- Digging a trench or pit in accordance with the markup, followed by pouring the foundation. To this end, the perimeter of the dug trench should be laid out in blocks, followed by pouring concrete or cement mixture.
- Removal of the formwork, followed by the erection of the walls of the greenhouse structure with your own hands from a material with positive thermal insulation characteristics. The best option is the use of hollow polystyrene-based thermoblocks. All wall masonry should be reinforced with metal.
- The process of wall insulation, in which block joints must be carefully coated with a high-quality waterproofing solution, and all cavities must be filled with special mounting foam. To achieve the maximum insulating effect, a foil thermal insulation film is fastened to the inner wall side.
For the purpose of year-round heating, it is advisable to think over the installation of underfloor heating under the screed, as well as pay attention to the artificial lighting device in the greenhouse structure. At the final stage, the roof frame is built under the covering material.

If the construction of the underground greenhouse is done correctly, then the built structure must have the following parameters and qualities:
- the presence of a bucket shape like \__/;
- a slight elevation of the northern wall above the southern one;
- slope indicators - no more than forty degrees;
- strong and heat-insulated walls;
- the presence of high-quality drainage ditches;
- reliable roofing.
Greenhouse without heating (video)
If all the above requirements are met, the durable construction of the greenhouse, made by oneself, will work on the principle of a thermos and delight the owners with a consistently high yield all year round.