What is OSAGO - where did it come from, what principles is it based on and how does it work. The emergence and development of OSAGO in Russia When OSAGO was introduced
When issuing or renewing OSAGO policies, drivers get some discount for insurance services for accident-free driving.
The amount of the discount depends on the CBM coefficient and the class of the driver.
To determine these indicators, it is necessary take into account a number of data about the driver and vehicle.
The concept of KBM
KBM - "Coefficient Bonus - Malus". This indicator determines the amount of the discount for accident-free driving, thanks to which an experienced and careful driver can significantly reduce the amount of insurance payments under the OSAGO policy.
The higher the CBM coefficient, the smaller the driver's discount, and vice versa.
Indicator entered into force in 2003.
 Initially, it was tied exclusively to the vehicle, that is with the purchase of a new car, the driver lost all past discounts when renewing the OSAGO policy.
Initially, it was tied exclusively to the vehicle, that is with the purchase of a new car, the driver lost all past discounts when renewing the OSAGO policy.
Since 2008, the KBM has been assigned personally to the driver and kept by him when changing cars, thus he began to fulfill his main function - to encourage accident-free driving.
When a driver transfers from one insurance company to another, the discount is also reserved for him.
There is a single table by which you can determine the size of the driver's KBM for the next year, taking into account his class.
All information about the driver's insurance contracts concluded by him from 01/01/2011 contained in the automated PCA database(Russian Union of Motor Insurers).
KBM is not used, or automatically equals one in the following situations:
- Upon initial receipt of the OSAGO policy, or the absence of information about the past insurance history in the database.
- In case of transit when insurance is issued for the period of travel to the place of registration, or to the place of technical inspection.
- In the case of registration of the car, registered abroad.
Calculation of discounts for OSAGO
The final amount of the discount provided for the OSAGO policy directly depends on the class of the driver.
When calculating the client class, insurers take into account the following data:

During the initial registration of an insurance policy, the driver is assigned class 3 with a coefficient equal to 1.
For each year of accident-free driving, the driver receives a 5% discount.
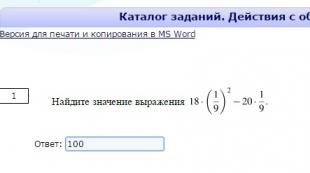
For example, driving for 4 years without accidents through his own fault, the driver receives a 20% discount on insurance (5% * 4 years of driving experience).
In the event of an accident, the driver's class is lowered, and his MSC coefficient is increased.
Accordingly, when calculating the insurance discount when renewing the policy or switching to another insurer, these data will be taken into account, which will reduce the discount.
The maximum amount of the discount for careful driving is 50% .
Drivers with a similar discount have 0.5 KBM coefficient and belong to the 13th grade.
This discount is available to drivers who for 10 years of driving have never been involved in an accident.
Calculation of BMF for several drivers
If several drivers are included in the OSAGO policy, then the KBM is calculated as follows:

The procedure for determining the CBM by insurers
From July 1, 2014, insurers can find out all the necessary information about the driver from the automated system of the Russian Union of Motor Insurers ( AIS RSA).
This information base contains all the data on the driver's previous insurance contracts concluded by him since 01/01/2011.
To verify the data, it is enough for the representatives of the insurer enter customer's driver's license number.
 The creation of such a resource allows avoid fraud by car owners when the driver deliberately tries to hide information that downgrades and increases the MSC.
The creation of such a resource allows avoid fraud by car owners when the driver deliberately tries to hide information that downgrades and increases the MSC.
At the moment, the insured can learn everything about the driver from the AIS RSA both when applying for a new policy and when changing the insurance company.
All data and data changes entered into AIS RSA only by insurance companies.
The PCA itself does not have the right to enter or change information.
Representatives of the insurance company are obliged to enter the necessary information into the database within 1 working day after the conclusion of the OSAGO agreement with the client.
When selling a policy, insurers must take into account all data on the driver's class and the MSC coefficient.
A discrepancy between the data about the driver and the discount assigned to him may result in penalties for the insurer.
It is important to consider that when determining the class, insurers take as a basis the class determined by last expired insurance contract, and the amount of insurance payments under previous contracts that ended no more than a year ago.
How to return KBM
Periodically, there are situations in which the car owner discovers a decrease in the discount on insurance when absence in his driving history of an accident for the relevant period.
To return the KBM, you must do the following:

Get a response from the RSA (the term for consideration of the application is 3-4 months).
- Send an application to the current insurer with a copy of the answer from the PCA attached.
- After the recalculation made by the insurance company revise the OSAGO contract and get back the overpaid funds.
Thus, when receiving a discount for accident-free driving, drivers should pay attention to the following points:
- KBM is an indicator by which the discount for accident-free driving is calculated.
- The higher the CBM coefficient, the smaller the discount.
- The size of the KBM directly depends on the class of the driver.
- The amount of the discount does not change when changing the insurance company or a car, since it is assigned to the driver.
- For multiple drivers assigned to the same vehicle, the BMR is calculated based on the driver with the lowest score.
- For an unlimited circle of KBM persons, the amount of the discount depends on driving history of the car owner.
- All data about the driver is available to insurers in a single database of AIS RSA.
- Invalid data can be corrected by the driver through the current insurer, by submitting an application to the PCA.
Read more:
4 comments
help is required to return the cbm (v.u 16 TN131926 expiration date and replacement with a new v.u 16 18 043971 replacement on 08/21/2014) the control is accident-free, the right to drive the a.m is issued for one, this a.m (as well as 2 previous a.m. m) were not used as a taxi.
addition to the above (dated 03/04/2016) on 04/08/2014 I purchased an a.m-l largus in the a.s. In the same car dealership, the OSAGO-company Nasko was registered. After 1 year, when registering the OSAGO, but already in another Asco company, I was told that my CBMs were canceled in Nasko. (I repeat OSAGO 2013-2014 was issued for VAZ-15, Max company and it also turns out that this company has ceased operations), otherwise they are not responsible. As a result, for 12 years my cbm is 10% instead of relying 60%!!!
Hello!!! I have been driving since 2006 without accidents (ugh 3 times), I am insured annually without interruptions. In 2014 there was an accident, but not my fault. The next time I was insured in October 2016, I was told that a 5 percent discount is provided. I began to wonder what it was connected with, they told me about KBM. Before that, somehow I didn’t even know what it was and didn’t attach any importance to it. And now, when I got into it, I understand that you can have a good discount. I have kept insurance policies from 2012, from 2010 to 2012 I was insured in Alfa Insurance. Tell me, what document to get from Alfa-insurance, that I was insured with them and did not participate in an accident? And how to correct your KBM in the PCA (so that it is calculated from 2010) with the received documents in Alfa Insurance and the old OSAGO forms of other insurance companies in your hands? In 2013, I am right (10 years have passed).
The most important thing to remember about the OSAGO policy is that it compensates for the losses and damage that it was you, and not another entity, caused to a third party - the vehicle, the life and health of the passengers who were in it.
By insuring your civil liability, in the event of an accident, you save yourself from compensation for damage. The losses incurred by the subject as a result of your actions will have to be reimbursed by the insurance company.
As for you, your car, property, life and health, OSAGO does not cover these factors. To compensate for the damage caused to you personally, you will have to use your savings.. If you want to protect your vehicle from damage and theft, then you need to pay attention to the CASCO policy.
Each driver must buy an OSAGO policy, or at least be signed up for it. This law is valid even when you simply drive your car from a car dealership to a place of residence or registration (the exception is cases when the OSAGO policy involves an unlimited number of people who have the right to drive a car).
Without an OSAGO policy, you are not only deprived of the right to leave the roadway (in case of violation, a fine is provided - from 5 to 8 minimum wages), you also cannot register your car with the traffic police. In addition, in the event of an accident, you will have to compensate for considerable damage.
When driving, you should always carry the original policy with you., as well as the rights and documents of ownership of the car. If the policy is available, but you, for example, forgot it at home, the inspector has the right to send the car to a fine parking lot. You can return it from there only with the help of a policy.
In what year did it appear and become mandatory in the Russian Federation?
The history of OSAGO insurance dates back to the end of the 20th century, when it received the status of compulsory. In the 1920s, there were too few cars in Russia for an auto insurance initiative to be considered and approved at the state level. Only at the end of the 60s the number of cars increased so much that the issue of insurance was discussed at the level of the Council of Ministers.
In 1984, the Decree “On measures for the further development of state insurance and improving the quality of the work of insurance bodies” was legislatively approved, which became the basis for the creation of an “auto-combi”.
This is an insurance contract drawn up by a citizen on a voluntary basis, while the object of insurance is not only the car, but also passengers and their belongings.
Further development of auto insurance took place already in Russia. From what year did the introduction of OSAGO policies begin and when were they actually introduced, that is, “autocitizenship” became mandatory?
In 1991, CASCO was introduced on a voluntary basis, but it was not widely used. Since 1993, draft laws on mandatory auto insurance have been sent to the State Duma.
Employees of the Russian Insurance Supervision and the Department of Transport were preparing a draft of the corresponding legislative act. The period of consideration, study and integration of the law was quite long, the act came into force only in the summer of 2003, when compulsory auto insurance was introduced, and implementation was carried out in several stages.
When will the "autocitizenship" be canceled?
In turn, the Ministry of Finance has chosen a strategy for the development of the insurance sector in the country. Aleksey Moiseev, director of the organization, talks about replacing the classic OSAGO with other types of insurance.
Officials of the department suggested that it is necessary to gradually abandon compulsory insurance, as this is a direct restriction of the rights and freedoms of citizens. The law will determine which risk should be covered by an insured event.
The bill on the introduction of a tariff corridor is still under consideration so nothing concrete can be said. The Russian Auto Insurance Union has not yet commented on this situation.
Expert forecast
From the point of view of the situation in Russia and in the world, it can be said that the law will be adopted with a probability of 90%. Now the main trend is human freedom, which means that bills will adapt to this canon so as not to create a tense situation in the country.
If we track the dynamics of changes in legislation over the past few years, we can notice an interesting trend.
All "mandatory" documents receive the status of "voluntary" (issued at will), however, penalties for violation increase several times. This is a kind of “law violation tax”, which will help to avoid recidivism on the part of citizens.
When will they raise?
A fragment from the provisions of the traffic rules on fines for driving without insurance in 2018 - according to clause 2.1 of the Rules of the Road, each driver driving a car must keep the following documentation with him:
- driver's license of the corresponding category;
- registration documents for the car;
- OSAGO insurance policy.
It is not necessary to carry a diagnostic card, which confirms the passage of a technical inspection, as well as a power of attorney to drive a car - since 2012, this document may not even be drawn up.
Penalties can be charged both for each item separately, and in the form of an additional fine if all conditions are not met. Currently, the fines are:

The fine for driving a motor vehicle without insurance in 2018 in your own car is exactly the same as in someone else's!
Since March 2018, they began to consider an amendment to the bill, which provides not only a fine of 800 rubles (which is planned to be increased to 3,000 rubles), but also administrative penalties in the form of corrective labor for up to two weeks, deprivation of the right to drive a vehicle.
These sanctions are applied in the event of a repeated violation of the law or if an emergency situation entailed severe consequences, such as death, causing moderate or severe bodily harm to the subject, damage to monuments or other objects of historical importance, and in some other cases. The bill was approved in the first reading, and the second is scheduled for June 2018.
How much can you make a policy?
It should be noted right away that it is more profitable to purchase a compulsory insurance policy for the whole year at once. Getting insurance for a couple of months is more expensive. The price of annual car insurance corresponds to the figures indicated in the policy and does not change during the year, even if the price of insurance increases.
There is always a chance to make insurance for a couple of months and pay extra only if necessary, extending the period of use. The insurance period is divided into several parts.
Thus, when making an application, you can calculate the entire insurance year in advance (two months in winter, one in summer, three in autumn, etc.). At the time of payment, only the total number of months in a calendar year is taken into account.
What to do after the deadline?
 Many documents have a period of validity, at the end of which, securities lose their legal force, and OSAGO is no exception: (?). And legal sanctions for this case are also provided.
Many documents have a period of validity, at the end of which, securities lose their legal force, and OSAGO is no exception: (?). And legal sanctions for this case are also provided.
Failure by the driver of a vehicle to fulfill the obligation established by the federal law on insurance of his civil liability, namely driving a motor vehicle, if such compulsory insurance is known to be absent, will result in the imposition of an administrative sanction in the amount of 800 rubles. (as amended by Federal Laws No. 116-FZ dated June 22, 2007, and No. 196-FZ dated July 23, 2013). The reason for appealing the fine may be valid circumstances (force majeure, technical problems of the car, disability). We talked in detail about whether it is possible to drive a car after the expiration of the OSAGO and what will happen for it.
You need to contact the insurance company to either issue a new(read about how to renew the policy online, in we talked about how many days before the end of the insurance you can apply for a new one). Some firms offer customers who have issued a policy with them discounts on a new one, in other words, they go to a meeting, because they are interested in profit from customers, and customers in obtaining favorable insurance conditions.
Despite the fact that the document was mandatory for more than 50 years, the world is moving to a new stage of development, where there will be no place for obligations, but only supply and demand that will regulate the situation in the insurance services market.
Moreover, the legislation of the Russian Federation is already undergoing drastic changes, so you need to remember that the execution of the document is mandatory now, but who knows what will happen tomorrow. While the law is in force, it must be observed, which means:
- Issue OSAGO on time to avoid unnecessary expenses in case of an accident.
- Keep with you all the necessary documents in case of an accident.
- Do not use an expired policy.
- Dispute fines only when you think you are 100% right.
Use our online calculator to calculate OSAGO online - compare prices in various insurance companies. Save between RUB 1,498 and RUB 3,980 as the base rate can vary by 20%. No need to go to the office - you will receive an insurance policy to your e-mail
Obey the rules of the road and remain polite to other motorists, then you will definitely not have problems in the event of an accident or an accident.
Every year, a huge number of new drivers appear on the roads, just starting to learn the rules of the road and delving into the intricacies of driving. Deep study of traffic rules, passing an exam for admission to driving a car.
And here they are - the right to drive the vehicle. It remains only to get insurance and you can safely drive on the public road. However, not every future motorist knows when OSAGO was introduced in Russia. But the history of the emergence of autocitizen is very interesting.
The history of auto insurance development dates back to 1898, only 3 years after the invention of the first car. But this was not a mandatory procedure, but a voluntary one.
At that time, the Travels Insurance Company became the first company to enter the insurance path, having concluded the world's first vehicle insurance contract. The first owner of the insurance was a certain Martin Truman.
The cost of the policy was $ 12, and in the event of an insured event, the insurer was entitled to compensation in the amount of $ 500. In those years it was quite a lot of money. It is noteworthy that Truman purchased auto insurance against a collision of a miracle wagon at his disposal with a horse-drawn carriage, and not with another mechanical type of vehicle, of which there were very few at that time.
A little more than three decades, it took the United States auto industry to build up a sufficient number of vehicles required for the introduction of insurance as a mandatory procedure during the purchase of a vehicle.
The first prototype of mandatory auto insurance was introduced in Massachusetts in 1925. A little later, this concept began to develop in other regions of the United States, and by the mid-30s of the 19th century, European countries also adopted the baton called OSAGO. Already after the 50s of the 20th century, auto-citizenship became the generally accepted norm for all developed and many developing countries.
The beginning of auto-civil history in Russia
Contrary to common prejudice, the idea of creating mandatory insurance policies appeared in the Russian Federation quite a long time ago.
According to many experts, insurance in the Russian Federation appeared in 1924, exactly one year before the introduction of auto citizenship in the United States.
But due to the small number of mechanical vehicles in the then USSR, this idea from the leaders who ruled the Soviet Union was considered irrelevant, although very interesting from the point of view of protecting road users and making a profit in the country's treasury.
In the 60s, a much more serious direction appeared in the field of motor third party insurance. During this period, the development of the Soviet version of the auto-citizen falls. However, this attempt to introduce compulsory auto insurance was not successful either.
It was only in 1993-94 that the first real bills on autocitizenship began to be considered at meetings of the young State Duma.
Again, due to the lack of awareness and incompetence of the relevant authorities, the development of this type of insurance was very slow. And only in 2000 the final bill was adopted in the first reading.
After that, it was rapidly finalized, and on April 25, 2002, the country was able to get acquainted with the first one. True, he began to act only 15 months later - on July 1, 2003.
The first reaction to the emergence of compulsory auto insurance was perceived by motorists very negatively, because now they were forced to spend their money on purchasing a policy. Today, an auto citizen is commonplace, and her presence sometimes helps to restore the vehicle's performance in the event of an accident.

Tariffs 2014 and 2015
What you need to know about OSAGO?
From the moment when vehicle insurance became mandatory, the draft law “On OSAGO” has undergone a lot of changes, a huge number of amendments have been made to it.

What are we paying for?
Among the features of the autocitizen, I would like to highlight several important points:
- The rules for concluding agreements on auto citizenship, tariffing are regulated by the Government and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- As in many European countries, in our autocitizen there are such concepts as "Europrotocol" and "Direct compensation for damage." Thanks to the Europrotocol, drivers have the opportunity to file an accident without involving employees of the departmental structure of the State traffic inspectorate. Direct compensation means claiming compensation for the damage caused as a result of an accident directly from your insurance company, where the motorist has concluded a contract. Both in the first and second cases, there are some factors that exclude the possibility of using these services: more than two cars were involved in an accident, during the accident harm was caused to the health and life of the participants. In this case, both participants must have valid OSAGO policies with them. For several years, a huge minus of the domestic “direct reimbursement” was that it was more of an alternative version of auto citizenship. Whereas in foreign countries this type of insurance and payment of compensation is uncontested. That is, the injured party has the choice of which company to apply for compensation in the event of an insured event - to his own or the other participant in the accident. But often the freedom of choice turned against motorists, as the UK tried to send their client to a third-party company. The amendments to the Federal Law “On OSAGO” introduced on August 2, 2014 changed the current situation.
- When concluding an auto insurance contract, a flexible system of discounts works, increasing depending on the number of years of accident-free service - the so-called "bonus-malus" coefficient. For every accident-free 12 months of driving, the discount increases by 5%. If there are accidents that occurred due to the fault of the motorist, the amount of the premium increases depending on the number of accidents in the past insurance year.
Billing Features
The effectiveness of the autocitizenka for both parties to the contract, the driver and the insurer, by and large depends on the charging systems used. A correctly chosen tariff system allows you to correctly calculate the cost of a car insurance policy.
Even a slight change in the driver's initial data, coefficients can significantly affect the final cost of insurance.
Unlike , when choosing, the choice of risks is completely excluded, and the quality and correctness of the calculation depends on the competence of the service manager and on well-chosen coefficients.
In 2015, the first increase in tariffs took place, which led to an increase in the cost of the insurance contracts themselves.
As of today, the maximum allowable amount payable to the party injured as a result of a traffic accident is 400 thousand rubles. for each damaged car and 500 thousand rubles. - when causing harm to life and health of people.
The following factors influenced the change in the tariff system:
- high level of inflation;
- rising prices for medical care;
- the growing cost of spare parts and components for cars, as well as services for repair and restoration work.
How is OSAGO calculated?

Changes as of April 2015.
Tariffs, coefficients used to calculate the amount of insurance premiums for car insurance are regulated by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
According to the legislative framework, tariffs are a single settlement system for any insurance company that has a license to distribute OSAGO policies and is liable to insurers. True, from 10/11/2014, insurers were allowed to vary the basic fixed tariff rates, but within a certain limit.
Today on the Internet there are a lot of different online calculators that allow you to calculate the preliminary cost of insurance. This makes it possible to obtain information regarding the benefits of acquiring this type of service in a particular UK.
To find out the cost of an insurance policy in real time, you must have with you information about the vehicle, its owner, as well as persons admitted to driving, if contractual obligations are drawn up on the condition that the list of drivers is limited.
Coefficients used in calculating the cost of an auto citizen
included in the insurance contract.
For machines with high power, this coefficient is greater.
Outcome
At the end of the publication, I would like to summarize a little:
- The history of the development of motor insurance as a compulsory type of insurance has been in force since April 25, 2002. But in fact, the date of its launch began a year later.
- Basic tariffs are regulated by the legislation and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. They may be different in different SCs, however, the size is insignificant.
- When calculating, several basic coefficients are taken into account, depending on the age and length of service of the motorist / motorists, on the accident-free record, on the territorial attachment of the future owner / owners of the motor vehicle.
What is your attitude to OSAGO insurance? Are the insurance conditions offered by the state suitable for you?
Today, the presence of insurance is a habitual obligation of every motorist. The policy is perceived as one of the necessary pieces of paper in a set of driver's documents. But it was not always so.
Emergence of the auto insurance system in Russia
The introduction of insurance in the domestic auto world, in comparison with many foreign countries, started not so long ago.
Auto insurance owes its history to the United States. It is understandable, because it was in this country that the car was invented. Following individual episodes of voluntary insurance, some states in America already in the 20s of the XX century legalized compulsory auto insurance. The whole country followed suit. This practice soon became widespread in Europe.
Compulsory auto insurance appeared in the US shortly after the first accidents
In Russia, they started talking about compulsory insurance much later - in the second half of the 20th century. And they switched from talk to action only in 1984, when the corresponding act of the Council of Ministers of the USSR was adopted. And then it was about voluntary insurance. This step did not bring any significant results.
The issue of introducing insurance policies began to be discussed more actively at the government level after the collapse of the USSR. The development of market relations, the increase in the availability of vehicles contributed to an increase in the intensity of car traffic, and hence the accident rate on the roads. In addition, inclusion in the processes of globalization required the country to participate in many international agreements. In particular, the availability of compulsory auto insurance was one of the requirements for joining the WTO.
All this could not but push the legislators to introduce the OSAGO system. Moreover, the legal foundations for this were laid in 1996 by the first edition of the Civil Code. Liability insurance was provided for by Article 931 of the Civil Code.
Adoption of the OSAGO law: goals and history
The OSAGO law appeared as a result of many years of work with the participation of many government agencies. The bill was first submitted to the State Duma for discussion in 2000. The first version of the law "On Compulsory Insurance of Civil Liability of Vehicle Owners" was approved on 25.04.2002. Its entry into force was postponed for 15 months, so that car owners have the opportunity to navigate the new realities and conclude an insurance contract.
In 2005, the OSAGO law was submitted for discussion in the Constitutional Court. The initiators were the deputies, who considered that it contradicts the current legislation, the tariffs are too high, and the payments do not cover the possible risks. However, the court did not satisfy their demands.
OSAGO tariffs to this day remain a debatable issue for legislators, insurers and car owners
The purpose of the introduction of the law remains unchanged to this day. Classical insurance protects, first of all, the insured himself and his property in case of adverse events for him in order to compensate for the harm received. Motor third party liability insurance aims to cover damagesto other personsaffected by transport. According to the law, the perpetrator must pay the damage to the victims, but he does not always have the means to do this. And enforcement is troublesome and takes a lot of time.
The Law on Compulsory Third Party Liability Insurance solves several problems at once. The main ones are:
- Guarantee of payment to the injured party. The maximum size is set by law. To compensate for material damage, a limit of 400 thousand rubles was set, and for compensation for harm to the life and health of the victims - 500 thousand rubles. If the amount to be paid is exceeded, the difference is paid by the person responsible for the accident.
- Fixing payment terms. Today, the term for making a decision by the insurance company is 20 days.
- Unification of conditions. Despite the huge choice of insurers in the OSAGO market, the car owner can be sure that the contract is concluded according to standard rules.
- Insured protection. If the insurance company is experiencing financial difficulties or ceases to exist, the OSAGO agreement still remains in force, only the obligations are transferred to the Russian Union of Motor Insurers.
- Tariff predictability. Base rates are regulated by the state, and insurers are limited by limits.
- Responsibility of car owners. Legislators believe that a driver without OSAGO in the event of an accident through his fault runs the risk of leaving the victims without compensation. Therefore, the violator is held liable under Article 12.37 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, for which a fine of 800 rubles may be charged. And if there is a policy that has expired, or the document is not with him, then the person will pay 500 rubles in accordance with Article 12.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses.
The cost of insurance since the adoption of the law to this day is the most controversial issue. The state is trying to strike a balance between the interests of car owners and insurers. In each case, the price depends on the brand, condition and year of manufacture of the car, region, length of service and age of the insured, his driving history.
Main changes in OSAGO legislation
Since the adoption of the law on OSAGO, it has undergone many changes. Practice made its own adjustments to the development of insurance conditions. In 2018, the 42nd edition was adopted, which will come into force on June 1, 2019.
A significant block of amendments to the law was adopted in 2014. The main changes were:
- OSAGO ceased to apply to all types of trailers, with the exception of trailers for towing;
- the functions of financial policy in the field of OSAGO were transferred to the Central Bank of Russia;
- amended the procedure for termination of contractual relations and return of insurance;
- the procedure for processing documents for an insurance company without the participation of the traffic police according to the "Europrotocol" has been clarified.
The current OSAGO system is the same in all insurance companies
Since 2015, Russian auto insurance has been supplemented with a pleasant innovation for car owners - it has become possible to conclude a contract remotely, and an electronic policy has been equated to a paper document. This practice was used before, but traffic police officers, referring to a gap in the legislation, issued fines.
Further reform led to the next set of changes that appeared in 2017-2018 and are reflected in the current version. The reform touched upon the following aspects:
- Compensation in kind has been established as a priority for compensation of harm to victims. This form is aimed at combating the activity of "traffic lawyers", who, through long litigation, sought insurance payments in inflated amounts. From now on, the insurance company pays for the repair of the affected vehicle at the car service station, with which the insurer has an agreement. Monetary compensation is reserved for a limited number of cases (harm to life and health, mutual guilt, a significant amount of damage, etc.);
- tariffs have increased, which is aimed, firstly, at compensating for the unprofitability of insurance activities, and secondly, at increasing the limit of insurance payments;
- The minimum insurance period is limited to one year.
Some changes will only take effect in 2019. From October 2019, the conditions for reimbursement under the “European Protocol” will change, and the limit of insurance payments will also be increased without the involvement of the traffic police. And insurers will have the opportunity to deviate from base prices upwards up to 130% from September 2019 and up to 140% from 2020.
Given the relatively young history of auto citizenship, there is every reason to believe that the growth of competition between insurance companies, increasing the legal literacy of drivers and judicial practice will continue to inspire the deputies, that is, representatives of the legislature, to search for optimal solutions to effectively reform the auto insurance system.
Even novice motorists know that before driving on the streets of the city, it is necessary to take out insurance. There is a fine for not having an OSAGO policy. Additional costs increase the cost of already expensive car maintenance and cause dissatisfaction among citizens.
But the law on "autocitizenship" was adopted not at all out of a desire to collect more money from the population. Consider from what year OSAGO was introduced in Russia, and what purpose was pursued.
Prerequisites for the development of the law
Thanks to economic reforms in the country, the number of cars on the roads increased dramatically in the 1990s. Accordingly, the number of accidents has also increased, where new and not very cars were damaged to varying degrees. Damaged vehicles require repairs, the cost of which can be very, very high. Who should pay for it? According to civil law, any damage caused to someone else's property must be fully compensated for by those responsible for causing it. In other words, the person responsible for the accident should pay for the repair of someone else's car broken in an accident. Unless he can prove that he acted under extreme necessity or force majeure.
Given the low incomes of the population, in order to reimburse the cost of repairing an expensive new foreign car, the driver of another car had to part with a substantial amount of money, and sometimes with his own property: a car and even an apartment. There were examples of criminal cases when the cost of a mistake while driving was life.
Meanwhile, back in the first half of the last century in the United States began to insure the property liability of car owners. Such insurance made it possible to shift the burden of financial compensation from the driver to his insurance company. Europe also adopted useful experience, but in Russia, due to socio-economic reasons, it was not introduced, although such an idea was discussed in the USSR in the 60s.
However, at the beginning of the new century, it became obvious that it was necessary to introduce compulsory insurance not for the vehicles themselves, but for the liability of their owners. This will solve several acute problems at once:
- protect motorists financially;
- reduce criminal tension in society as a whole;
- make drivers more disciplined.
When OSAGO was introduced in Russia
It took quite a long time to develop all aspects of the new law - about 10 years. The first bills were submitted to the State Duma in 1993. However, consideration of the new normative act in the first reading took place only in 2000. Then two more years of improvements followed, and finally, in April 2002, the law was approved by the Federal Assembly and signed by the President.

However, OSAGO became strictly mandatory only a year later - from July 1, 2003. Such a long period of time was required to work out the mechanisms for implementing the new law and adopt the relevant documents. Subsequently, various amendments and additions were introduced, and in 2014 the OSAGO legislation was seriously reformed.
When car insurance first became mandatory, it caused a serious backlash from both drivers and insurance companies. Claims have been made that the new law severely restricts the rights of citizens and businesses to freedom of contract and property guaranteed by the Constitution. In addition, the cost of the policy turned out to be quite high for most car owners. But the Constitutional Court, having considered the appeal of a group of deputies, considered that the restrictions imposed by OSAGO do not contradict the basic law.
Features of compulsory insurance
The main feature of liability insurance for car owners is its obligation. And both for the drivers themselves and for insurance companies. To the displeasure of the latter, the state severely limits the size of the insurance premium by introducing a single mechanism for calculating it and a tariff corridor for all. Since 2016, insurers cannot even refer to the lack of the necessary forms - the policy has been issued electronically.
Unlike property insurance, OSAGO does not insure the car, but the liability of its owner or driver to third parties in the event of an accident. If someone else's car was damaged in an accident, then the insurer of the culprit will pay for its repair. If he does not have a policy, he himself makes the compensation.
When calculating the cost of insurance, such a coefficient as KBM () is taken into account. Its essence lies in the fact that a disciplined driver who behaves carefully on the roads and does not arrange accidents pays less and less at the conclusion of each subsequent OSAGO agreement. The difference can be up to 50%. Accordingly, an inverse relationship also operates - the repeated culprit of an accident will pay more every year.
Insurance indemnity under OSAGO is limited. The maximum that an injured driver can receive is 400,000 rubles. If this amount does not cover the cost of repairs, then the missing part will have to be recovered from the culprit on their own, as part of a civil lawsuit.
The introduction of OSAGO, although it caused a lot of controversy, made it possible to achieve the goals set. New amendments protecting car owners and expanding the ability of insurance companies to reward careful drivers come into force on July 1, 2018